Here, we would like to extend our sincere thanks to every distributor, wholesaler, project contractor, brand owner, and end-user who has chosen and trusted Jumei Acrylic Manufacturing Co., Ltd. as your acrylic sheet manufacturer and long-term supply partner. Your support has allowed our acrylic sheet products to be applied in more industries, more regions, and more creative projects across the world. Our acrylic sheets inspire creativity and enable innovative designs, making them the preferred choice for those seeking unique and artistic solutions. Customers can choose from a variety of features, colors, and options to customize their acrylic sheets for specific project needs.
Jumei Acrylic Manufacturing Co., Ltd. specializes in both cast and extruded acrylic sheet manufacturing.
Your trust inspires us to continuously improve our production capabilities, optimize product quality, and strengthen our service and logistics support. Our commitment remains unchanged — to provide each customer with stable, high-quality acrylic sheets and a reliable, worry-free cooperation experience. Jumei Acrylic uses 100% pure virgin raw material to ensure the best quality of our acrylic sheets. We also offer UV-protected acrylic sheets with a 10-year guarantee for outdoor use.
2025 Recap: At Jumei Acrylic, Quality Always Comes First
As a professional manufacturer specializing in acrylic (PMMA) sheets, Jumei Acrylic deeply understands that quality is never just a slogan — it is the result of strict standards, technology investment, and responsibility to our customers.
Throughout 2025, we continued to:
• Upgrade production equipment
• Optimize processing technology
• Select high-quality raw materials. Jumei Acrylic uses 100% pure virgin raw material to ensure the best quality.
• Strengthen inspection and testing systems
This ensures that every acrylic sheet from Jumei Acrylic delivers excellent optical clarity, surface smoothness, stability, and weather resistance — whether used for advertising, signage, lighting, displays, furniture, construction, industrial applications, or customized projects. Acrylic sheets can be customized in size and thickness to meet specific project requirements, allowing us to customize solutions for your needs. Our product range includes clear, colored, mar resistant, and bullet resistant acrylic sheets. Acrylic sheets are UV treated to prevent yellowing and fading, making them suitable for outdoor use. They are also lightweight and have a high impact resistance compared to glass, offering an outstanding strength-to-weight ratio.
We strictly control key indicators such as:
✔ Thickness tolerance
✔ Light transmittance
✔ Surface flatness
✔ Color consistency
Jumei Acrylic ensures strict quality control for uniform thickness, color, and performance across all batches. At the same time, we optimized packaging protection, cargo handling, and transportation planning — because we know that a stable supply chain is essential for your business success, and Jumei Acrylic is proud to be part of that foundation. Jumei Acrylic guarantees fast delivery within two weeks for most orders.
Thank You to Every Customer Who Works with Jumei Acrylic
In the past year, Jumei Acrylic sheets have been widely used in:
• Advertising & Display Systems
• Lightboxes & Signage
• Commercial & Interior Decoration
• Construction & Partition Panels
• Industrial Components
• DIY & Creative Works
• Furniture & Art Installations
Jumei Acrylic provides customized services, including OEM and ODM options for acrylic sheets, to meet diverse customer needs. Like leading companies such as E & T Plastics Mfg. Co., Inc., we offer a range of tailored acrylic solutions.
Every inquiry, every order, and every suggestion has encouraged us to keep improving. Your expectations motivate us to refine our craftsmanship and enhance our service.
To all our partners —
thank you for choosing Jumei Acrylic.
We are proud to customize our products and services to support your creativity and project requirements.
Thank you for growing with us.
Discover Our Acrylic Sheet Options
At Jumei Acrylic, we take pride in offering an extensive selection of acrylic sheets designed to meet the diverse needs of various industries and applications. Our clear acrylic sheets are the perfect choice for creating eye-catching displays, signage, and advertising materials that demand exceptional clarity and a glossy finish. For projects that require a splash of personality, our colored acrylic sheets come in a wide variety of vibrant colors, allowing you to match your unique vision and requirements.
We understand that every project is different, which is why our acrylic sheets are available in multiple thicknesses, finishes, and sizes. Whether you need a durable material for high-traffic areas, a glossy surface for premium displays, or a specific color to enhance your brand, we’ve got you covered. Our materials are widely used across industries such as retail, hospitality, and healthcare, thanks to their outstanding impact resistance, versatility, and long-lasting durability. No matter your application, you’ll find the perfect acrylic sheet option at Jumei Acrylic to ensure your project stands out.
Jumei Acrylic in Action: Industrial Applications
Jumei Acrylic sheets are engineered to excel in demanding industrial applications across a range of sectors. Our high-quality acrylic materials are trusted by clients in manufacturing, construction, automotive, and more, thanks to their superior durability, lightweight properties, and versatility. We offer custom colors and tailored designs to ensure our acrylic sheets seamlessly integrate into your specific projects and applications.
Our company is dedicated to providing solutions that not only meet but exceed the requirements of various industries. From impact-resistant panels for machinery to unique components for specialized equipment, our acrylic sheets are designed to enhance both performance and aesthetics. We work closely with our clients to understand their needs, delivering materials that are ideal for displays, signage, and industrial uses alike. With Jumei Acrylic, you can count on dedicated service, innovative designs, and materials that help your business achieve its goals.
Fast Delivery, Every Time
At Jumei Acrylic, we know that timely delivery is essential to keeping your projects on track. That’s why we are committed to providing fast delivery and reliable service for every order. Our advanced manufacturing facilities and strategically located warehouses enable us to offer a range of delivery options, including express shipping, so you receive your acrylic sheets and materials exactly when you need them.
We understand the importance of meeting deadlines, and our dedicated team works tirelessly to ensure your orders are processed and shipped quickly. Whether you’re facing a tight timeline or need to replenish your stock in a hurry, our company is here to support you. With Jumei Acrylic, you can trust that your materials will arrive on time, every time—because your success is our commitment.
Advanced Capabilities: Precision Laser Cutting
Jumei Acrylic is proud to offer advanced precision laser cutting services, enabling our clients to create custom-cut acrylic sheets tailored to their exact specifications. Our state-of-the-art laser cutting equipment delivers precise, clean cuts for a wide range of shapes, sizes, and intricate designs, making it easy to bring even the most complex projects to life.
Whether you need unique signage, detailed displays, or components with tight tolerances, our laser cutting capabilities ensure exceptional quality and accuracy. We work closely with our clients to provide innovative solutions that meet their project requirements, from one-of-a-kind prototypes to large-scale production runs. With Jumei Acrylic, you can count on easy customization, high-quality results, and a company dedicated to providing the best in acrylic sheet solutions. Let us help you create something truly unique with our precision laser cutting services.
2026 Vision: Jumei Acrylic Will Continue to Support Your Business
Looking ahead to 2026, Jumei Acrylic will remain committed to delivering value through quality, stability, and partnership. As part of our vision for the future, we are dedicated to ongoing innovation and development to shape the acrylic sheet industry. We draw inspiration from established leaders such as E & T Plastics Mfg. Co., Inc., whose professionalism sets a benchmark within the acrylic solutions sector.
Our focus will be on:
✔ Strengthening quality control and production stability
So every batch remains consistent and reliable.
✔ Expanding acrylic sheet categories and solutions
To better support advertising, architecture, industry, retail, and creative fields.
✔ Enhancing service efficiency and communication
Ensuring fast responses and smooth order follow-up.
✔ Promoting environmental responsibility
Supporting greener and more sustainable materials manufacturing.
At Jumei Acrylic, we firmly believe:
your growth is our mission.
From material consultation and sample testing to mass production and long-term supply, we will continue to stand beside you as a dependable acrylic sheet partner.
Work with Jumei Acrylic — Your Trusted Acrylic Sheet Manufacturer
If you are looking for:
⭐ Stable-quality acrylic sheets
⭐ A reliable manufacturer partner
⭐ Competitive and reasonable pricing
⭐ Professional support and responsive service
Jumei Acrylic welcomes you to continue working with us in 2026 and beyond. Our dedicated sales team is committed to supporting your needs, ensuring customer satisfaction, and helping expand your business. We offer an extensive inventory of wholesale clear acrylic sheets at competitive prices, similar to leading suppliers like A&C Plastics. Clear acrylic sheets are commonly used for POP displays, store fixtures, and glazing, while our colored acrylic sheets are available in over 60 colors—ideal for light boxes and creative applications. As a reliable acrylic sheet manufacturer, we provide customization options in various colors and thicknesses to meet your specific requirements.
Shop directly for acrylic sheets through our website for a convenient and user-friendly experience, with a wide variety of options available. For quotes, support, or more information, contact Jumei Acrylic today—we are ready to assist you with your next project.
A Final Thank-You from Jumei Acrylic
Thank you again for your trust and support throughout 2025.
In 2026, Jumei Acrylic will continue delivering high-quality acrylic sheets and attentive customer service to partners all over the world.
We sincerely wish you a successful, healthy, and prosperous New Year.
Let’s keep moving forward — together.
However, the consequences extend far beyond aesthetics. Over time, yellowing signals deeper durability concerns. This article aims to uncover the technical reasons and fixes behind acrylic yellowing.
What Is Yellowing?
Yellowing refers to the gradual change in color of plastics. The defect is quantified by the Yellowness Index (YI). It’s a standardized metric used across automotive, construction, and consumer goods.
Yellowing isn’t a mere cosmetic issue. Sectors like solar energy suffer from reduced light transmission, which lowers the energy yield. Discoloration in medical devices can compromise sterility and usability.
Why Do Acrylic Sheets Perform Comparatively Well?
Acrylic (PMMA) is more resistant to yellowing than many plastics like ABS, PVC, or polycarbonate. Its chemical structure is inherently stable against UV and oxidation.
Example: Acrylic windows in aircraft and aquariums retain clarity for 10–15 years. It outperforms polycarbonate sheet as an alternative to acrylic options for a custom project.
Extreme UV exposure, high heat, or chemical pollutants can still cause discoloration. Outdoor acrylic signage in tropical climates may show slight yellowing after 8–10 years.

Technical Causes of Acrylic Yellowing
01. UV Radiation and Photodegradation
- UV-Induced Chain Scission: Ultraviolet radiation breaks the carbon–carbon bonds in acrylic’s polymer chains. The unstable molecules initiate further reactions that degrade the polymer structure.
- Oxidation Reaction: Free radicals formed by UV exposure react with oxygen, creating color-producing molecular structures. They absorb visible light, leading to a yellow-to-brown tint.
02. Influence of UV Wavelengths
- UVB (280–315 nm) causes the most significant molecular changes, breaking bonds and accelerating chain scission.
- UVA (315–400 nm) is less energetic but penetrates deeper, contributing to long-term oxidation.
03. Thermal Degradation
- Excessive Heat During Service: Prolonged exposure above 80–90°C accelerates oxidation and causes thermal chain scission and depolymerization.
Acrylic exposed to 100°C for 1,000 hours shows a 40% reduction in light transmission.
- Heat Generated During Machining or Forming: Overheating during laser cutting, bending, or polishing induces internal stresses. They later act as weak points where oxidation and discoloration begin.

04. Chemical Exposure
- Solvents and Cleaning Agents: Alcohols, ketones, and ammonia-based cleaners interact with acrylic, causing surface crazing (fine cracks). They trap dirt and accelerate discoloration.
- Pollutants and Fumes: Nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) and sulfur compounds react with acrylic surfaces, forming yellowish films. Hydrocarbon vapors accelerate oxidation in urban or industrial zones.
05. Environmental Stress Factors
- Moisture and Humidity: PMMA is relatively resistant to hydrolysis. Still, high humidity accelerates UV-induced reactions. Water molecules can act as carriers for free radicals, intensifying chain scission.
- Microcracks and Oxidation: Moisture penetrates microcracks, allowing oxygen to diffuse deeper into the polymer matrix. It leads to localized oxidation and visible yellowing.
06. Mechanical Stress and Stress Cracking
- Stress Concentration: Areas under mechanical load degrade faster when exposed to sunlight or chemicals. Stress accelerates chain scission and oxidation.
- Residual Stress: Poor fabrication, such as improper cooling after thermoforming, leaves internal residual stresses. These act as weak points, making acrylic more susceptible to UV and chemical attack.
07. Material-Specific Factors
- Impurities as Catalysts: Trace metals, residual monomers, or contaminants act as catalysts for degradation, accelerating oxidation and discoloration.
- Recycled Acrylic: Contains shorter polymer chains due to prior processing. These chains are more prone to scission, leading to faster yellowing.
08. Additives and Acrylic Colors
- Clear Acrylic: More susceptible to yellowing since there are no pigments to absorb or scatter harmful radiation.
- Tinted or UV-Stabilized Acrylic: Performs better, but some dye components themselves degrade under UV, producing yellowish hues.
09. Extruded vs Cast Acrylic Sheet
- Cast Acrylic: Longer polymer chains, higher molecular weight, and fewer internal stresses. More resistant to yellowing.
- Extruded Acrylic: Shorter chains and higher residual stresses from continuous processing make it more vulnerable.

How to Identify Yellowing in Acrylic?
a. Visual Inspection
- Yellow Tint Comparison: The simplest method is to compare an aged acrylic sample against a new reference piece. Even slight discoloration becomes obvious when placed side by side.
- Loss of Gloss and Transparency: Yellowing often coincides with a dull surface finish and reduced light transmission. Acrylic that once appeared crystal-clear may look hazy or tinted.
b. Measuring Yellowing
- Yellowness Index (ASTM E313): The Yellowness Index (YI) is a standardized metric defined by ASTM E313 to quantify the degree of yellow discoloration in transparent materials.
- Xenon-Arc Testing: Simulates full-spectrum sunlight, including UV, visible, and infrared radiation. Widely used in automotive and aerospace industries to predict long-term performance.
- UV Fluorescent Testing: Uses fluorescent UV lamps (UVB or UVA) to accelerate degradation. Particularly effective for architectural and shop signage (different settings and shapes).
Detecting Yellowing Before It Becomes Severe
- Surface Cracks (Crazing): Fine cracks appear before visible yellowing in stressed areas.
- Haze Formation: Early oxidation causes light scattering, producing a cloudy appearance.
- Brittleness: Mechanical flexibility decreases, making acrylic prone to cracking under load.

Prevention Methods: How to Reduce and/or Avoid Yellowing?
Acrylic can stay clear for years with the right approach. Designers and any store with a stock should rely on technical strategies for their businesses to retain reputation before customers.
01. UV Stabilized or UV-Blocking Acrylic
- Stabilizer: UV absorbers like benzotriazoles filter harmful wavelengths. Meanwhile, HALS (hindered amine light stabilizers) scavenge free radicals, slowing chromophore formation and surface chalking.
- Outdoor Grades: Weather-resistant PMMA grades are engineered with higher UV stability and optimized molecular weight distribution, improving resistance to chain scission and long-term color shift.
02. Apply Protective Coatings
- UV Blocking Films and Laminates: Co-extruded or post-applied films attenuate UVB and UVA, reducing the rate of chain scission; they also act as sacrificial layers against pollution and abrasion.
- Weatherable Hardcoats: Cross-linked, abrasion-resistant coatings protect the surface from micro scratches that seed oxidation, and many include UV screening chemistries that slow color formation.
- Maintenance Advantage: Coated surfaces keep gloss longer and resist reactivity to common airborne pollutants (NO₂, SOx, hydrocarbons), lowering surface yellowing rates.
03. Proper Maintenance and Cleaning
- Recommended Cleaners: Use mild soap and water-based solutions with soft microfiber cloths to remove particulates without scratching.
- Avoid Reactive Agents: Do not use ammonia, alcohols, ketones, aromatics, or strong alkaline/acidic cleaners; these can cause surface crazing that traps dirt and accelerates oxidation.
- Rinse Protocol: Rinse thoroughly and dry to prevent mineral spots; do not dry-wipe dusty surfaces as pre-rinsing prevents micro abrasion.
04. Good Fabrication Practices
- Control Heat: During laser cutting, bending, and polishing, maintain recommended temperatures and feed rates; excessive localized heat creates internal stresses linked to later yellowing.
- Anneal to Relieve Stress: Post-fabrication annealing equalizes internal stresses, reducing stress cracking and the associated pathways for deeper oxidation.
- Edge Finishing: Use progressive grit and proper coolant to minimize heat-affected zones at edges, which are common sites of early tinting.

Optimal Design and Installation
- Minimize Intense UV Exposure: Orient panels to reduce midday UV load; integrate shading elements or overhangs where feasible.
- Enable Ventilation: Design for airflow behind panels and enclosures to dissipate heat; elevated operating temperatures significantly accelerate oxidation and depolymerization.
- Avoid Stress Concentrations: Use floating mounts, compliant gaskets, and proper hole sizing/edge distances to prevent point loads that catalyze stress cracking and localized yellowing.
- Seal Against Moisture: Seal edges and joints in high-humidity environments; microcrack infiltration increases oxidation depth and color formation.
Special Considerations for Outdoor Applications
a. Climates with High UV Intensity
- Tropical Regions: High humidity combined with intense UV accelerates photodegradation + microcracks. Acrylic signage in Southeast Asia often shows yellowing within 5–7 years if not UV-stabilized.
- Desert Climates: Extreme solar radiation and heat (>45°C daytime temperatures) cause thermal oxidation. In Middle Eastern skylights, acrylic panels can lose up to 20% light transmission in 8 years.
- High Altitudes: UV intensity increases by 10–12% per 1,000 meters of elevation. Acrylic used in ski resorts or Himalayan observatories faces accelerated chain scission and oxidation.
Recommended Grades for Extreme Sun Exposure
- Weather-Resistant PMMA: Special outdoor grades with UV absorbers (benzotriazoles) and HALS stabilizers are designed to withstand prolonged exposure.
- Tinted Acrylic: Lightly tinted or UV-blocking grades reduce radiation penetration, extending clarity.
- Expert Tip: For desert or tropical installations, specify cast acrylic with UV stabilizers, which can maintain transparency for 15–20 years compared to 8–10 years for standard extruded acrylic.
b. Applications with Constant Heat Source
- Heat Impact: LEDs generate localized heat that can raise acrylic temperatures to 80–90°C, accelerating oxidation and yellowing.
- Expert Tip: Use heat-resistant acrylic grades or apply hardcoats to minimize thermal degradation.
Sun-Drenched Skylights and Greenhouses
- Skylights: Continuous solar exposure combines UV and heat stress. In desert climates, skylights made of extruded acrylic may yellow within 5–7 years.
- Greenhouses: Acrylic panels exposed to constant sunlight and humidity face accelerated degradation. Light transmission drops by 12–18% after 10 years in humid tropical greenhouses.
c. Marine and Polluted Urban Environments
- Marine Environments: Salt spray and high humidity corrode surfaces, creating microcracks that trap pollutants. Acrylic boat windows often show yellowing within 5–6 years without protective films.
- Urban Pollution: Smog containing NO₂, SO₂, and hydrocarbons accelerates oxidation. In megacities like Delhi or Beijing, outdoor acrylic installations yellow 30–40% faster than rural counterparts.
Protective Films Recommended
- UV-Blocking Films: Reduce radiation penetration and act as sacrificial layers against pollutants.
- Weatherable Laminates: Provide dual protection against salt, humidity, and smog.
- Expert Tip: Apply multi-layer protective films and schedule annual cleaning with mild soap solutions.

Repair and Restoration: Can Yellowing Be Fixed?
Yellowing in acrylic ranges from superficial surface oxidation to deep discoloration. Glazing in plexiglass or product variety may not suffice for creativity, innovation, or success. Some specialty products (adhesives or equipment) can extend the life.
01. Surface Polishing
Light abrasive polishing removes the thin, oxidized surface layer where chromophores accumulate. It can restore gloss and slightly reduce apparent yellowing on the outer microns.
Start with fine abrasive (2000–3000 grit), progress to micro mesh or liquid polish for acrylic, then finish with a non-reactive plastic polish. Keep surfaces cool; use low pressure and avoid heat buildup.
02. Chemical restoration methods
Purpose-made acrylic polishes and fine compounds can fill micro scratches and remove surface films, and improve gloss. Some include mild cleaners that lift pollutant residues (NOx, SOx, hydrocarbons).
Alcohols, ketones, aromatics, and ammonia-based agents can cause crazing (fine cracking), extract additives, or embrittle the surface, accelerating oxidation and trapping dirt that worsens yellowing.
When to Replace from Top Acrylic Sheet Manufacturer?
- Deep Oxidation through Thickness: When chromophoric groups form throughout the sheet, color persists even after aggressive polishing. It coincides with haze, brittleness, or stress cracking.
- Performance Thresholds: Replace panels when visual yellowing is clearly noticeable, light transmission drops enough to affect function, or when mechanical integrity declines (crazing, edge cracks).
Indicators of Non-Recoverable Damage
- Persistent Tint after Polishing: Color returns quickly or never meaningfully improves.
- Haze + Brittleness: Reduced impact resistance and audible “crisp” sound during handling.
- Stress Whitened Areas: Yellowing around fasteners or tight mounts alongside microcracks.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1) Does all acrylic eventually yellow?
Yes. All acrylic can yellow over time, but the rate depends on UV exposure, heat, pollutants, and material grade. High-quality, UV-stabilized acrylic may remain clear for decades.
2) Why does outdoor acrylic yellow faster than indoor acrylic?
Outdoor acrylic faces direct sunlight, fluctuating temperatures, and pollution, which accelerate oxidation. Indoor acrylic, shielded from UV and pollutants, can last 20+ years with minimal yellowing.
3) Is polycarbonate more prone to yellowing than acrylic?
Yes. Polycarbonate yellows faster due to weaker UV resistance. Acrylic (PMMA) is preferred for clarity and long-term outdoor use, especially in skylights and signage.
4) Can LED lighting cause acrylic to yellow?
Yes. Constant heat from LEDs raises acrylic temperature, accelerating oxidation. Using heat-resistant acrylic grades or adding ventilation reduces this risk.
5) Does recycled acrylic yellow faster than virgin acrylic?
Yes. Recycled acrylic contains shorter polymer chains and impurities, which act as catalysts for degradation. Virgin cast acrylic resists yellowing better.
6) Can improper cleaning cause acrylic to yellow?
Yes. Cleaners with ammonia, alcohols, or aromatics cause surface crazing, trapping dirt and accelerating discoloration. Use mild soap and water instead to save time.
7) Why do aquarium panels yellow over time?
Aquarium acrylic faces constant moisture, UV from lighting, and chemical cleaners, which accelerate surface oxidation. Proper cleaning and UV-stabilized acrylic can extend clarity.
8) Can protective films stop acrylic yellowing?
Protective films with UV blockers and weatherable laminates significantly reduce yellowing, especially in marine and polluted urban environments.
Conclusion
Don’t neglect acrylic yellowing as a cosmetic issue. Deeper chemical/environmental interactions can compromise its exceptional strength, clarity, and performance in an extensive inventory. Implementing the proper measures can retain its impressive functionality for decades, even in the harshest climates.
Get the Best Acrylic with Zero Chances of Yellowing from JUMEI
Not many reliable manufacturers like Jumei Acrylic can guarantee zero yellowing with proper care. We’ve been serving the industry for years with satisfaction. Contact us to know more about acrylics.
]]>It’s no different for Acrylic, primarily in sectors associated with outdoor applications. Its UV resistance is a critical factor regarding longevity and aesthetics. So, explore how acrylic behaves under constant UV radiation.
What is UV Radiation?
Sunlight is a complex spectrum, including ultraviolet (UV) radiation. It’s the part of the electromagnetic spectrum immediately beyond visible violet light.
UV is capable of triggering chemical changes in polymers. It’s commonly divided into three bands, each with distinct implications for materials and outdoor use.
- UVA (315 – 400 nm): Dominates natural sunlight on Earth. Deeper penetration into polymers causes gradual photo-oxidation, yellowing, reduced gloss, and long-term aesthetic changes.
- UVB (280 – 315 nm): More energetic and strongly associated with chemical bond breakage. Less abundant at ground level, but still a major contributor to embrittlement and strength loss.
- UVC (100 – 280 nm): Highest energy but almost entirely filtered by the ozone layer. Relevant mainly in artificial environments (sterilization lamps), causing rapid + severe degradation.
How does UV Damage Plastics?
Photons excite electrons to form radicals, and polymer chains change irreversibly. Surfaces lose clarity and gloss, structures lose toughness, and products fail earlier than intended.

Effects on Molecular Structure (Laser Cutting)
Chain Scission: Breaks polymer backbones, reducing molecular weight. Lower molecular weight leads to decreased toughness and higher brittleness.
Oxidation: Introduces carbonyl groups and other oxygen-containing species, visible in spectroscopic analysis (carbonyl index increase). Oxidation promotes discoloration and surface embrittlement.
Discoloration: Chromophore formation shifts light absorption, producing yellowing or browning. Loss of transparency and gloss is common in clear polymers.
Global Perspectives with Real-Time Examples
Spectral Reality: UVC sterilization (254 nm lamps) causes rapid cracking and yellowing in unprotected plastics within days of exposure.
Climate Impact: High-UV regions (Florida, Queensland, high-altitude cities like La Paz) accelerate degradation. Elevated altitude and lower cloud cover increase UV intensity, shortening service life.
How Acrylic Responds to UV Exposure?
Acrylic demonstrates superior UV resistance under natural and artificial light compared to many plastics. Still, its performance depends on grade, environment, and protective additives.
01. Natural UV Resistance of Acrylic
Acrylic is chemically known as polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). It has an inherently stable molecular structure to resist UV-induced chain scission. Acrylic maintains clarity and strength for extended periods.

02. Resistance to Yellowing (Abrasion Resistant)
Acrylic resists yellowing because the polymer lacks aromatic rings to absorb UV strongly. PMMA’s structural integrity disperses UV energy without forming chromophores that cause discoloration.
Standard acrylic can last 5–10 years outdoors before noticeable yellowing. UV-stabilized grades with absorbers or coatings can extend lifespan to 15–20 years, blocking up to 99% of harmful UV rays.
Conditions accelerating yellowing:
- High UV index regions (tropical climates, high altitudes).
- Poor-quality extruded acrylic vs cast acrylic.
- Prolonged exposure to pollutants and high humidity.
03. Mechanical Performance Under Sunlight
Damaging UV rays can reduce mechanical strength over time. Still, lightweight acrylic retains rigidity better than many plastics.
- Impact Strength: Acrylic has less impact resistance than polycarbonate but maintains stability under UV light.
- Rigidity + Flexibility: Long-term exposure may slightly reduce flexibility, but acrylic avoids potentially severe embrittlement.
- Standard Acrylic: 5–10 years outdoors before mechanical decline.
- UV-Stabilized Acrylic: 15–20 years with minimal loss in tensile strength.
04. Optical Clarity Retention for Clear Acrylic Sheets
One of acrylic’s greatest strengths is its ability to maintain optical clarity under prolonged UV exposure.
- Fresh Acrylic: 92% visible light transmission, comparable to glass.
- After 10 Years of UV Exposure: Still 88–90% transmission, with minimal haze.
- UV-Blocking Grades: Specialized acrylic sheets can block up to 99% of ultraviolet light.
Factors Influencing UV Resistance in Acrylic
a. Cast Acrylic vs Extruded Acrylic
- Cast Acrylic (PMMA): Produced by pouring liquid monomer into molds and polymerizing. Exhibits higher molecular weight, better chemical resistance, and superior UV stability. Commonly used in architectural glazing, skylights, and outdoor signage.
- Extruded Acrylic: Manufactured by continuous extrusion, resulting in a lower molecular weight. More economical but less resistant to UV degradation. Tends to yellow or lose mechanical strength faster under prolonged sunlight.
b. Specialty UV-Stabilized and UV-Blocking Grades
- UV-Stabilized Acrylic: Contains stabilizers that absorb harmful wavelengths, extending lifespan to 15–20 years outdoors.
- UV-Blocking Acrylic: Designed to block up to 99% of UV radiation, protecting sensitive applications like museum displays, artwork, and solar panel covers.
c. UV Absorbers and Stabilizers
- UV Absorbers (Benzotriazoles, Benzophenones): Incorporated during manufacturing to absorb high-energy UV photons before they damage the polymer backbone.
- Antioxidants: Complement UV stabilizers by reducing oxidative degradation.
- HALS (Hindered Amine Light Stabilizers): Neutralize free radicals formed during UV exposure, slowing oxidation and chain scission.
- UV-Resistant + Chemical Resistant Coating: Applied to acrylic sheets or products to enhance surface protection for UVA light.
- Hard-Coat Layers: Improve scratch resistance while adding UV stability, common in automotive headlamps and outdoor lenses.

d. Intensity of Sunlight by Region/Climate
High UV Index Regions: Tropical zones (Florida, Australia) experience UV indices of 10–12, accelerating degradation. High-altitude cities (La Paz, Bolivia) receive stronger UV due to a thinner atmosphere.
Moderate UV Regions: Northern Europe and Canada, where acrylic products last longer due to lower UV intensity.
e. Temperature Fluctuations and Outdoor Pollution
Temperature Swings: Expansion and contraction stress acrylic, especially when combined with UV-induced oxidation.
Pollution: Airborne chemicals (ozone, NOx, SO₂) accelerate surface crazing and discoloration.
f. Humidity and Saltwater Exposure
- Marine Environments: Salt spray and high humidity amplify UV degradation.
- Acrylic boat windows in coastal regions often require UV-stabilized grades to prevent hazing within 5–7 years.
g. Thickness
- Thicker acrylic sheets absorb more UV energy before it penetrates deeply, slowing degradation.
- Thin Sheets (<3 mm): More prone to yellowing and mechanical weakening.
h. Acrylic Colors and Pigments
- Opaque or Tinted: Pigments act as UV blockers in frosted, matte, glitter, etc, to reduce penetration.
- TiO₂ (Rutile Grade): Highly effective pigment for UV screening in opaque acrylic.
- Carbon Black: Provides near-total UV protection in dark-colored or painted sheets.
Comparison: Acrylic vs Other Common Alternatives Under UV
Acrylic generally outperforms most common alternatives in UV resistance. It’s more or less the same for polycarbonate, PVC, PETG, and ABS.
01. Acrylic vs Plexiglass
Definition: Plexiglass is a brand name for acrylic (PMMA). Chemically, they are the same material.
UV Resistance: Both share acrylic’s natural UV stability. Cast grades last 10–20 years outdoors with minimal yellowing.
Example: Outdoor signage in Europe often uses Plexiglass sheets, which retain clarity for over a decade.
02. Acrylic vs Glass
Glass: Inorganic, naturally UV-resistant, but standard soda-lime glass blocks only 25–30% of UV radiation.
Acrylic: Blocks more UV (up to 12× better) for half the weight of glass, while maintaining 92% transmission.
Applications: Museums prefer UV-blocking acrylic glazing to protect artwork, since glass allows more UV penetration.
03. Acrylic vs Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate (PC): Extremely impact-resistant but highly UV-sensitive. Without coatings, PC yellows and loses clarity within 2–3 years outdoors.
Acrylic: Superior UV resistance, retaining clarity for 10–20 years.
Use PC for safety barriers where impact strength matters, but apply UV-resistant coatings. For signage or glazing, acrylic is the better choice.

04. Acrylic vs PVC
PVC: Prone to UV degradation, chalking, and brittleness unless heavily stabilized.
Acrylic: Naturally resists yellowing and maintains clarity.
Example: PVC pipes exposed outdoors often become brittle within 2–5 years, while acrylic roofing sheets last much longer.
05. Acrylic vs PETG
PETG: Tough and flexible, but poor UV resistance. It tends to haze and lose clarity within 1–3 years outdoors.
Acrylic: Maintains transparency and UV stability for a decade or more.
Applications: PETG is favored for retail displays and packaging, while acrylic dominates outdoor signage and glazing.
06. Acrylic vs ABS
ABS: Strong and versatile but highly UV-sensitive. It discolors and becomes brittle quickly under sunlight.
Acrylic: Far superior in UV resistance, retaining clarity and mechanical stability.
Example: ABS housings for electronics often yellow within a few years, while acrylic display panels remain clear.
Applications Involving Acrylic’s UV Resistance

a. Outdoor Signage and Display Panels
Outdoor signage is constantly exposed to direct sunlight, rain, and pollution, making UV resistance critical.
Acrylic’s ability to resist yellowing and maintain color stability ensures that branding and advertising remain visually appealing over time.
Example: In Dubai, where UV indices regularly exceed 11, outdoor acrylic billboards maintain vibrant colors for years.
b. Skylights, Greenhouses, and Architectural Glazing
Architectural applications demand long-term transparency and structural stability under sunlight. Acrylic excels in these roles by default.
Greenhouses: Acrylic panels allow maximum light penetration for plant growth while blocking harmful UV wavelengths that damage crops.
Example: In Northern Europe, greenhouses use UV-blocking acrylic to protect delicate plants while ensuring optimal photosynthesis.
c. Marine and Automotive Components
Marine and automotive environments combine high UV exposure, humidity, and saltwater, creating one of the harshest conditions for materials.
Marine use: Acrylic windows and hatches on boats resist UV-induced hazing and saltwater corrosion, lasting 10+ years in coastal climates.
Automotive applications: Acrylic is used in headlamp covers, sunroofs, and decorative trims, where clarity and UV resistance are essential.
d. Consumer Products
Outdoor furniture: Acrylic tabletops and decorative panels resist yellowing and maintain gloss, unlike PVC or ABS, which chalk and crack.
Lighting fixtures: Outdoor lamps and decorative lighting use acrylic covers to ensure clarity and UV stability.
Home décor: Acrylic picture frames and garden ornaments retain transparency and aesthetics even in direct sunlight.
Global example: In Australia, acrylic furniture and lighting fixtures are preferred for their long-term clarity and resistance to UV degradation.

Testing and Standards for UV Resistance
Validating UV resistance is about simulating years of sunlight, heat, and moisture in weeks or months. The standards below are widely used by plastics, coatings, and glazing industries to predict service life.
01. ASTM G154
Standard practice for operating fluorescent bulbs or UV lamp apparatus (UV-A or UV-B) to expose nonmetallic materials. Alternating cycles of UV exposure and moisture, with controlled temperature and irradiance.
Typical cycles –
- UV-A 340 nm lamps: 8 h UV at 60–70°C + 4 h condensation at 50–60°C.
- UV-B 313 nm lamps: Shorter wavelength, harsher; used when a stronger degradation driver is desired.
02. ASTM D4329
Fluorescent UV exposure specifically for plastics (leverages practices in G154, adds plastics-focused guidance). Aligns test conditions, specimen preparation, and evaluation with polymer requirements; improves reproducibility across labs.
Typical reporting: Exposure hours (500–2000 h), lamp type, irradiance setpoint (0.68 W/m² at 340 nm), cycle parameters, and pass/fail criteria tied to property retention.
03. ISO 4892
Methods of exposure to laboratory light sources for plastics; choice depends on whether you want to simulate direct sun, behind-glass light, or accelerated UV only.
04. ISO 4892-2 (Xenon Arc)
Spectrum: Full solar spectrum (UV+visible+IR) with filters for “daylight” and “behind glass”. Includes water spray and humidity control; best for correlation to real outdoor exposure.
05. ISO 4892-3 (Fluorescent UV)
Spectrum: UV-focused (UV-A/UV-B) for accelerated photodegradation screening. Faster, more cost-effective, and strong for ranking materials and stabilizer systems.
Xenon arc vs UV Fluorescent Testing
- Xenon Arc: Closest to natural sunlight; better for predicting the field performance of colorants, coatings, and clear plastics.
- UV Fluorescent: Emphasizes short-wavelength UV; accelerates chemical damage, ideal for screening and worst-case UV stress.
- Xenon: More sophisticated humidity/spray control; captures hydrolysis, swelling, and thermal effects.
- Fluorescent: Condensation is strong for surface wetness but less realistic for driven weather cycles.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1) Is acrylic naturally UV-resistant?
Yes. Cast acrylic (PMMA) has inherent UV resistance, maintaining clarity for 10–20 years outdoors. Extruded acrylic is less durable without stabilizers.
2) Does acrylic block harmful UV rays?
Standard acrylic blocks some UV, but UV-blocking grades can filter up to 99% of UV radiation, protecting artwork, signage, and interiors.
3) How long does acrylic last in direct sunlight?
With UV stabilization, acrylic can last 15–20 years outdoors before noticeable yellowing or haze. Standard grades may degrade within 5–7 years in high-UV regions.
4) Does acrylic yellow under sunlight?
Acrylic resists yellowing better than most plastics. Cast acrylic remains clear for over a decade, while extruded grades may yellow faster in tropical climates.
5) Can acrylic crack or warp due to UV exposure?
UV alone rarely causes cracking, but combined heat and stress can lead to warping or crazing. Proper installation with expansion joints prevents this.
6) Does colored acrylic resist UV better than clear acrylic?
Yes. Pigments act as UV blockers, so tinted or opaque acrylic sheets often last longer outdoors than clear sheets.
7) What cleaning methods protect acrylic from UV damage?
Use mild soap and water with microfiber cloths. Avoid ammonia or alcohol-based cleaners, which weaken the surface and accelerate UV degradation.
8) Can UV-resistant coatings extend acrylic’s lifespan?
Yes. Anti-UV coatings and films can add 5–10 years of durability, especially in harsh climates like deserts or coastal regions.
Conclusion
Acrylic’s story under sunlight is one of resilience and reliability. It stands out as a material of clarity and endurance. Its natural UV resistance, combined with stabilizers and protective coatings, makes it a trusted choice for applications.
Best Acrylic Sheet Manufacturer with UV Filtering at JUMEI
Not many acrylic manufacturers can secure optimal UV protection for acrylic sheets. That’s where Jumei Acrylic is ready to serve with years of experience. Contact us to know how our sheets meet your needs.
]]>However, collaborating with the right manufacturer ultimately makes the difference. This article digs up the leading producers with redefining standards with cutting-edge technology for absolute quality.
Modern Acrylic Sheets: Properties and Applications
Material Composition
Acrylic sheets are primarily made from PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate). PMMA is a transparent thermoplastic from natural gas. It’s known for optical clarity, weather resistance, and ease of fabrication.
Different Types of Acrylic Sheets
- Cast Acrylic: Clear acrylic sheets that harness easy machinability; ideal for high-end applications.
- Extruded Acrylic: More cost-effective with consistent thickness; notably suitable for mass production.
- Abrasion-Resistant Acrylic: Well-coated for scratch resistance; applied in high-contact environments.
- Impact-Modified Acrylic: Enhanced toughness to survive various applications, used in safety barriers.
- Tinted and Colored Acrylic: Available in an extensive range of hues for decorative and/or branding purposes.
- Textured Acrylic: Provides reasonable privacy with noteworthy aesthetic appeal in architectural design.
Acrylic sheets are marketed under brand names like Plexiglass, Perspex, and Lucite. Such names make the material more specifically recognizable worldwide.

Key Properties of Clear Acrylic Sheets
- Transparency: Acrylic sheets transmit up to 92% of visible light, outperforming glass in clarity.
- Strength and Impact Resistance: They are 17 times more impact-resistant than glass, making them safer for public installations.
- Lightweight: Acrylic weighs less than half of glass, reducing transportation and installation costs.
- Weather Resistance: Superior UV and moisture resistance ensure long-term outdoor use without yellowing.
- Ease of Fabrication: Can be cut, drilled, thermoformed, and polished with standard tools, enabling custom sizes.
- Chemical Resistance: Resistant to many acids and bases, though vulnerable to solvents like acetone.
Hallmarks of Top Acrylic Sheet Manufacturers
Manufacturing Excellence
Leading manufacturers employ precision casting and extrusion for consistent thickness, clarity, and durability. Enhanced casting methods enable superior optical clarity compared to traditional extrusion.
Product Range and Laser-Cutting Customization
Top producers offer clear, glitter, matte, colored, textured, impact-modified, and UV-resistant sheets. Each one caters to diverse industries from construction to healthcare. Customization options include –
- Cut-to-size full sheets for specific architectural projects.
- Special coatings (anti-reflective, abrasion-resistant, UV-blocking).
- Brand-specific colors and textures for retail and advertising.
CLAREX cell-cast acrylic sheets allow tailored solutions with anti-reflective coatings and diffusive features for electronics and optics. Customization is a major demand driver across Asia.
Top manufacturers like Jumei Acrylic offer bespoke solutions for the signage and packaging industries. They perfectly reflect regional (up to local) branding, signage, and advertisement needs.

Innovation and Research and Development
- Technological Breakthroughs: Innovations include enhanced casting techniques, eco-friendly formulations, and nanocoatings that improve scratch resistance and longevity.
- Sustainability Focus: R&D is increasingly directed toward bio-based acrylics and recycling processes to meet global environmental standards.
- Industry Transformation: Aerospace applications highlight innovation. Stretched acrylic sheets in cockpit canopies offer 300% higher impact resistance than glass, reducing aircraft weight by 400 kg per F-35 jet.
- Expert Insight: Manufacturers investing at least 5% – 7% of revenue into R&D tend to lead in market share, as innovation drives differentiation.
Quality Assurance and Testing
- Multi-Stage Testing: Leading firms implement 5-step quality control systems, including raw material inspection, dimensional accuracy checks, and optical clarity verification.
- Global Standards: Certifications such as ISO 9001 and SGS weather resistance tests ensure compliance with international benchmarks.
- Expert Tip: Buyers should prioritize makers with transparent quality documentation. Such measures reduce risks in high-stakes applications like medical barriers or aerospace glazing.

Key Innovations in Acrylic Sheet Manufacturing
Enhanced Performance Features
Modern acrylic sheets are engineered to outperform traditional glass and plastics through specialized coatings and formulations. Some noteworthy examples include –
- Anti-Scratch and Abrasion-Resistant Coatings: Advanced nanocoatings extend sheet life in high-contact environments like retail displays and public transport.
- UV Protection and Weatherability Improvements: UV-stabilized sheets prevent yellowing and degradation, maintaining clarity for 10+ years outdoors.
- Enhanced Impact Resistance (Bullet-Resistant): Impact-modified acrylic can be up to 17x stronger. Such acrylic is used in bank teller windows, military vehicles, and secure facilities.
- Fire-Rated and Flame-Retardant Formulations: Fire-rated acrylic meets UL 94 standards, reducing risk in construction and transport.
- Anti-Fog and Anti-Static Treatments: Anti-fog coatings are critical in medical incubators and refrigerated displays. Anti-static sheets prevent dust accumulation in cleanrooms and electronics manufacturing.
Sustainability Initiatives
Global manufacturers are investing heavily in eco-friendly practices to align with circular economy goals. You’re guaranteed to encounter one or more of the following –
- Recycled Acrylic Options: Recycled PMMA reduces reliance on virgin petrochemicals.
Example: Lucite International has launched recycled acrylic for signage and furniture markets.
- Energy-Efficient Manufacturing Processes: Modern extrusion lines consume 20% – 30% less energy through automation and heat recovery systems.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint Initiatives: Global leaders like Mitsubishi Chemical report 15% lower CO₂ emissions by optimizing logistics and production.
- Bio-Based Acrylic Alternatives: R&D is exploring bio-PMMA derived from renewable feedstocks like sugarcane. Bio-based acrylic could capture 10% of the market by 2030.
- Waste Reduction and Recycling Programs: Manufacturers recycle offcuts and defective sheets into pellets for reuse.
Example: European Union mandates a minimum 30% recycled content in plastics by 2030, pushing innovation in acrylic recycling.

Advanced Processing Technologies
Precision Cutting and CNC Machining: CNC routers achieve ±0.1 mm accuracy, enabling complex architectural designs.
Laser Cutting and Engraving Services: Laser technology allows intricate patterns for luxury retail displays and signage.
Thermoforming and Bending Innovations: Sheets can be thermoformed into complex 3D shapes without losing clarity.
Digital Printing and Coloring Techniques: UV digital printing enables photo-quality graphics directly on acrylic sheets.
Smart Manufacturing: Industry 4.0 integration allows real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and AI-driven quality checks.
Digital Integration and Customer Service
- Online Product Configurators and Design Tools: Clients can select thickness, color, and finish online, reducing design cycles.
- Digital Sample Ordering and Visualization: Augmented reality (AR) tools let customers visualize acrylic sheets in real-world settings.
- Supply Chain Transparency and Tracking: Blockchain-based tracking ensures authenticity and sustainability compliance.
- Technical Support and Design Consultation: Manufacturers offer virtual consultations for architects and engineers, speeding up project approvals.
- Fast Turnaround and Just-in-Time Delivery: AI-driven logistics reduce lead times by 15% – 20%, ensuring on-demand supply for industries.

Selecting the Right Acrylic Sheet Manufacturer
Evaluation Criteria
- Industry Experience and Reputation: Established manufacturers with 10+ years of experience often have proven track records in delivering consistent quality.
Look for manufacturers with strong export histories. It’s because global reach often signals reliability and compliance with international standards.
- Product Quality and Consistency: Acrylic sheets should meet ISO 9001 quality standards and pass optical clarity, thickness uniformity, and impact resistance tests.
Consistency is critical for industries like aerospace and healthcare, where safety and performance cannot be compromised.
- Diverse Range and Customization Options: Leading manufacturers offer cast, extruded, UV-resistant, impact-modified, flame-retardant, and colored sheets (blue, gold, iridescent).
Customization includes cut-to-size, coatings (anti-scratch, anti-fog), and specific opaque colors. Jumei can provide tailored solutions for retail and architectural clients to save time.
- Technical Expertise and Customer Support: Manufacturers with in-house R&D teams and technical consultants can guide clients on material selection, fabrication, and installation.
Most of the Asia-based customer support often includes on-site training for fabricators, ensuring proper handling of acrylic sheets.
- Pricing Structure and Value Proposition: Transparent pricing models that balance cost with durability and performance are essential.
Avoid focusing solely on a low price. Instead, carefully consider lifecycle costs. It’s because high-quality sheets reduce replacement frequency for designers, company, and businesses.

Questions to Ask Potential Manufacturers
01. Manufacturing Processes and Quality Control Measures
Ask: Do you use cast or extruded methods, and how do you ensure thickness consistency?
Leading firms employ multi-stage inspections, including optical clarity and weather resistance testing.
02. Lead Times and Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs)
Global manufacturers typically offer 2 – 6-week lead times depending on customization. MOQs vary; some suppliers require 500 – 1000 sheets, while others cater to smaller orders for niche industries.
03. Customization Capabilities and Limitations
Ask about color matching, coatings, and thermoforming options.
Example: Retail chains often demand brand-specific colors, which only advanced manufacturers can deliver consistently.
04. Certifications and Compliance Documentation
Look for ISO 9001, UL 94 flame ratings, SGS weather resistance tests, and REACH compliance. Aerospace and medical industries require FAA and FDA certifications, respectively.
05. Technical Support and After-Sales Service
Ask: Do you provide design consultation, installation guidance, and troubleshooting support?
Example: European suppliers often offer virtual consultations for architects and engineers.
06. Sample Availability and Testing Options
Request samples for scratch resistance, UV stability, and impact strength tests before committing to bulk orders.
Always test samples under real-world conditions (outdoor exposure, chemical contact).

Red Flags to Avoid
- Lack of Transparency About Materials and Processes: If a manufacturer cannot explain whether sheets are cast or extruded, this signals poor technical standards.
- Inconsistent Product Quality or Poor Reviews: Negative feedback on optical clarity, yellowing, or brittleness is a warning sign.
Example: Some low-cost suppliers in emerging markets have faced criticism for inconsistent thickness and poor UV resistance.
- Limited Technical Knowledge or Support: Manufacturers unable to provide technical datasheets or fabrication guidance may not meet industry demands.
- Unrealistic Pricing (Too Low May Indicate Poor Quality): If pricing is 30% – 40% below market average, it often reflects inferior raw materials or a lack of quality testing.
Market Insight: The average price of high-quality cast acrylic is USD 3 – 4 per kg. However, low-cost alternatives in stock may fall below USD 2 per kg.
- Poor Communication or Unresponsiveness: Delayed responses or vague answers to technical queries indicate weak customer service.
How to Work with Your Acrylic Sheet Manufacturer for the Best Outcome?
Specification and Ordering Process
How to Specify Your Requirements Accurately: Define dimensions, thickness, color, finish (frosted or translucent), and performance features (UV resistance, fire rating). Always provide CAD drawings or digital mockups to avoid misinterpretation.
Example: A construction firm in Dubai specifies UV-stabilized sheets with 12 mm thickness for outdoor signage to withstand desert heat.
Understanding Technical Data Sheets and Specifications: Manufacturers provide TDS (Technical Data Sheets) detailing optical clarity, tensile strength, impact resistance, and thermal expansion.
Acrylic sheets typically transmit 92% of visible light, outperforming glass. Compare TDS across suppliers to ensure compliance with ISO 9001 and ASTM standards.
Sample Evaluation and Testing: Request samples for scratch resistance, UV stability, and impact strength.
Example: Retail chains in Europe test acrylic samples under 24-hour UV exposure chambers before approving them for store displays.
Prototype Development and Approval Process: Manufacturers often provide prototype sheets or mockups for client approval. Automotive firms prototype headlight covers using impact-modified acrylic before mass production.

Fabrication and Installation Support
Partnering with Manufacturers That Offer Fabrication Services: Some manufacturers provide CNC cutting, laser engraving, and thermoforming services.
Example: Japanese suppliers offer precision laser engraving for electronics casings.
Installation Guidelines and Best Practices: Acrylic sheets expand with temperature; allow 3–5 mm expansion gaps per meter during installation. Use non-abrasive cleaning agents to avoid surface damage.
Stadium skylights in Europe use special mounting systems to accommodate thermal expansion.
Maintenance and Care Recommendations: Clean with mild soap and water, avoid ammonia-based cleaners. Polish scratches using specialized acrylic polish kits.
Expert Tip: Schedule annual inspections for outdoor installations to check for UV degradation.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Cracking: Often due to improper drilling—use special acrylic drill bits.
- Yellowing: Indicates poor UV stabilization; replace with UV-resistant sheets.
- Warping: Caused by uneven installation or excessive heat exposure.
Building Long-Term Partnerships
Benefits of Establishing Relationships with Manufacturers: Long-term clients often receive priority service, faster lead times, and dedicated support.
Example: Aerospace firms maintain exclusive contracts with acrylic suppliers for cockpit canopy production.
Volume Discounts and Contract Opportunities: Bulk orders can reduce costs by 10–20%, especially for construction and retail projects.
Expert Tip: Negotiate annual supply contracts to lock in pricing and ensure availability.
Access to New Products and Innovations: Partnering with leading manufacturers provides early access to bio-based acrylics, anti-scratch coatings, and smart sheets.
Example: European automotive firms gained early access to flame-retardant acrylic sheets for interior panels.
Priority Service and Dedicated Account Management: Top manufacturers assign account managers to handle technical queries, logistics, and after-sales support.
Case: Large aquarium projects in Asia benefit from dedicated teams ensuring delivery of extra-thick cast acrylic panels.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What makes a top acrylic sheet manufacturer stand out?
A top acrylic sheet manufacturer stands out through consistent product quality, advanced R&D, global certifications, and customer-focused innovation, ensuring reliability across industries.
- Are acrylic sheets better than polycarbonate sheets?
Yes. Acrylic sheets offer superior optical clarity (92% light transmission) and better scratch resistance. Meanwhile, polycarbonate excels in impact strength. The choice depends on application needs.
- How long do acrylic sheets last outdoors?
High-quality UV-stabilized acrylic sheets can last 10–15 years outdoors without yellowing or losing clarity. It makes them ideal for signage and construction.
- Can acrylic sheets be recycled?
Yes. Many manufacturers now offer recycled PMMA sheets, supporting circular economy practices and reducing environmental impact.
- What thickness options are available for acrylic sheets?
Acrylic sheets range from 1 mm to 50 mm in thickness, with custom options available for specialized applications like aquariums or aerospace glazing.
- Are acrylic sheets safe for food contact?
Food-grade acrylic sheets comply with FDA and EU regulations, making them safe for use in food displays, containers, and protective barriers.
- How do manufacturers ensure quality consistency?
Top manufacturers use multi-stage testing, including optical clarity checks, impact resistance tests, and weatherability trials to meet ISO and ASTM standards.
Conclusion
Choosing the right acrylic sheet manufacturer isn’t some random procurement decision. It makes your investment worth it in terms of quality and innovation for long-term success. The best manufacturers also deliver confidence, reliability, and vision with the sheets.
Get the Top Acrylic Sheets for Your Projects at JUMEI
Jumei Acrylic is one of the few options within major suppliers. You’re guaranteed to meet satisfaction. Contact us to reach our experienced experts with a commitment to possibilities and creativity for ideas.
]]>A compelling visual setup can elevate mood, reinforce brand identity, and spark engagement. Acrylic stands out for its clarity, durability, and elegance. Innovative setups with creative acrylic displays can transform spaces immediately.
Exclusive Benefits of Acrylic Displays
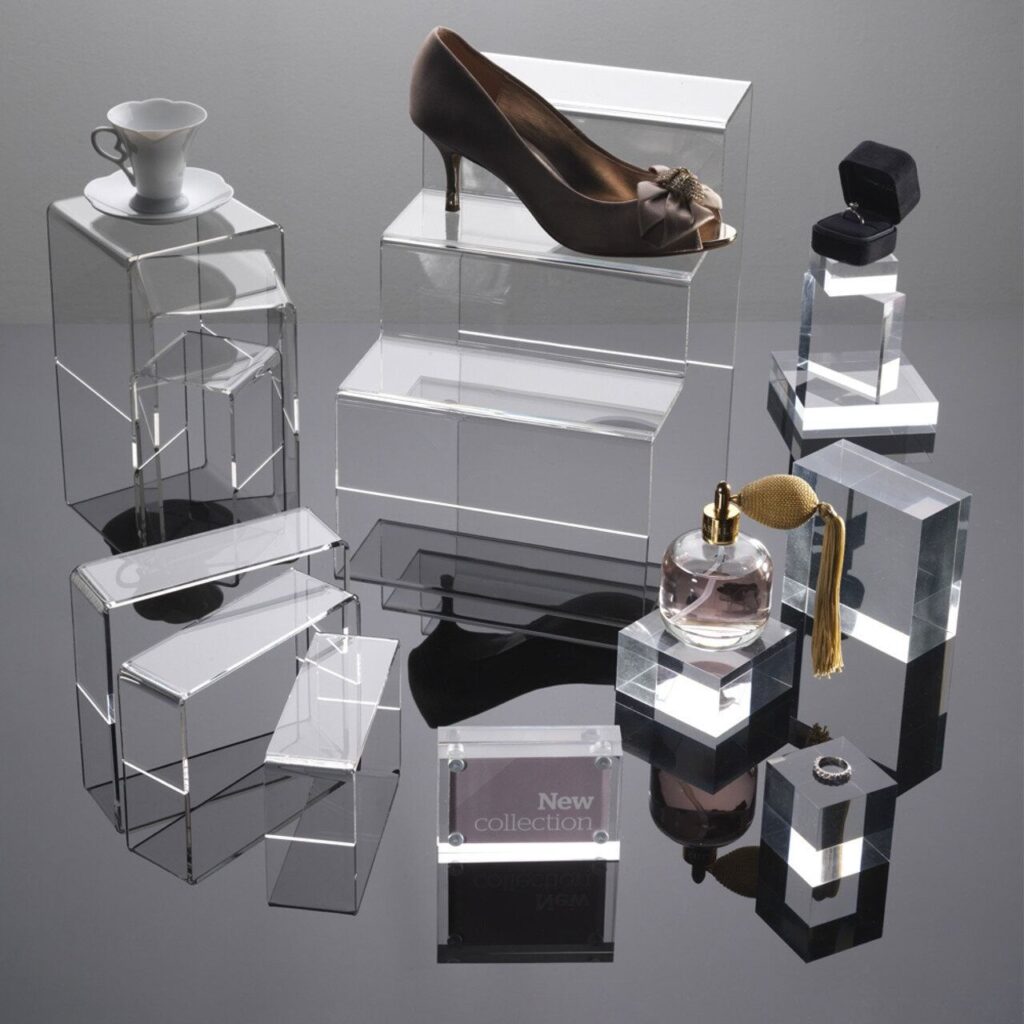

a. Visual Clarity and Elegance
Acrylic’s crystal-clear transparency rivals glass but with added resilience. Such clarity allows products, signage, or décor items to stand out without visual obstruction. It’s ideal for retail displays, museum exhibits, and minimalist home setups.
Experts often dub acrylic as “plastic glass”. It’s because the thermoplastic can transmit up to 92% of visible light. It’s one of the most transparent alternatives available within most project budgets.
b. Durability and Safety
Unlike glass, acrylic is impact-resistant and shatterproof. Acrylic plexiglass is safer and more reliable in high-traffic or outdoor environments.
Acrylic is 17 times more impact-resistant than glass, reducing the risk of breakage and injury. In outdoor exhibitions at the Melbourne Convention Center, acrylic sheets withstood weather fluctuations and heavy traffic.
c. Lightweight and Easy to Move
Acrylic’s lightweight nature makes it ideal for portable setups, pop-up shops, and trade shows. It’s the go-to choice for anything that involves frequent rearrangement.
Acrylic weighs less than half of glass, making transportation and installation significantly easier. Brands at international expos often choose acrylic for modular booth designs that can be assembled and disassembled quickly without specialized tools.
d. Customizable and Versatile
Acrylic can be laser-cut, UV-printed, thermoformed, or edge-lit. That’s where you’ll get endless creative possibilities.
Design options are available in clear, frosted, colored, mirrored, and even LED-illuminated formats. Jewelry brands use colored acrylic blocks to match seasonal themes, while tech expos use illuminated acrylic signage to attract attention.
e. Cost-Effective Longevity
Acrylic displays offer long-term value with minimal upkeep. They resist yellowing, scratching, and weathering, making them a smart investment.
Businesses report up to 40% longer lifespan for acrylic displays compared to traditional materials like wood or cardboard.

Different Types of Acrylic Displays
Acrylic displays come in diverse forms to suit specific requirements. Each one can elevate visibility, organization, and aesthetics across retail, events, homes, and offices when appropriately installed.
01. Acrylic Sign Holders and Frames
They’re more like mandatory elements in restaurants, offices, and retail counters for showcasing menus, promotions, or artwork.
Opt for double-sided holders in high-traffic areas to maximize visibility. Clear signage increases customer engagement by up to 30% in retail environments.
02. Acrylic Display Stands
Tiered and multi-level stands are ideal for presenting products with hierarchy and elegance. Jewelry stores in Dubai and Tokyo use tiered acrylic stands to highlight premium pieces without visual clutter.
Use black or frosted acrylic for luxury items to create contrast and focus. Acrylic cosmetic displays have been shown to boost product interaction by 25% in beauty retail setups.
03. Acrylic Boxes and Cases
These protective yet stylish enclosures are used to display delicate or high-value items. Museums in Berlin and Seoul use UV-resistant acrylic cases to preserve artifacts while maintaining visibility.
Acrylic’s impact resistance makes it ideal for safeguarding collectibles without the fragility of glass. Add lockable lids or LED bases for added security and flair.

04. Acrylic Wall Panels and Shelves
Wall-mounted acrylic solutions combine storage and style, perfect for modern homes and retail interiors. IKEA’s modular acrylic shelving systems are popular in urban apartments.
Use floating acrylic shelves to create a clean, gallery-like display for books, plants, or merchandise. Transparent shelving reduces visual clutter and enhances perceived space, especially in small rooms.
05. Tabletop and Counter Displays
Compact and customizable, these displays are perfect for receptions, trade booths, and personal décor. At CES Las Vegas, tech brands use acrylic tabletop displays to showcase gadgets with embedded QR codes.
Choose modular designs that allow quick updates for seasonal or campaign changes. Counter displays influence impulse purchases in 60% of retail transactions.
06. Custom and Thematic Acrylic Designs
From engraved panels to illuminated logos, custom acrylic designs offer branding and personalization. Luxury brands like Chanel and Apple use edge-lit acrylic signage in stores to reinforce brand identity.
For weddings/parties, personalized acrylic nameplates or centerpieces add elegance and memorability. Acrylic can be laser-cut into logos, shapes, or thematic motifs, available in PMS-matched colors and LED-integrated formats.
Displays for Different Occasions and Spaces
Acrylic displays adapt beautifully across retail, corporate, event, hospitality, and personal spaces. You can expect optimal clarity, elegance, and branding power in every setting.
a. Retail and Commercial Spaces
Acrylic displays are a staple in retail environments for showcasing premium products with sophistication and clarity. Examples: Jewelry risers, cosmetic tiered stands, and promotional signage.
Retailers using acrylic displays report up to 30% higher product engagement due to improved visibility. Use tiered acrylic stands to create visual hierarchy and maximize shelf space.

b. Corporate Offices
In professional settings, acrylic adds polish and brand cohesion through signage, awards, and organizational tools. Examples: Desk nameplates, brochure holders, branded wall panels.
Combine frosted acrylic with engraved logos for a premium, understated look. Offices with branded acrylic elements see a 15% – 20% boost in visitor perception of professionalism.
c. Events and Exhibitions
Portable, customizable, and elegant, acrylic displays elevate the ambiance and branding of any event. Examples: Podiums, illuminated signage, display cases for products or awards.
Use clear acrylic podiums for speakers to maintain visual openness while adding prestige. Exhibitors using acrylic signage report 25% more booth traffic compared to traditional materials.
d. Restaurants and Cafés
Acrylic enhances the dining experience by presenting menus and promotions with clarity and style. Examples: Tabletop menu holders, promotional inserts, decorative panels.
Use angled acrylic holders to reduce glare and improve readability under ambient lighting. Clear menu displays can increase upsell rates by 12% – 18% in casual dining environments.
e. Homes and Personal Spaces
Acrylic adds a minimalist, modern touch to home décor while offering practical organization. Examples: Wall-mounted shelves, makeup organizers, photo frames, desk accessories.
Use acrylic drawer inserts for organizing cosmetics or stationery without visual clutter. Transparent organizers improve daily task efficiency by 20% in home offices.

f. Hospitality and Service Environments
Hotels, salons, and service desks benefit from acrylic’s clean look and branding flexibility. Examples: Front desk signage, nameplates, brochure racks, and room number panels.
Use backlit acrylic panels for nighttime visibility in lobbies or outdoor service counters. Branded acrylic signage contributes to higher guest satisfaction scores in hospitality surveys.
Creative Design Ideas to Elevate Space with Acrylic Displays
01. Mix Transparency with Color Accents
Acrylic’s inherent clarity makes it a perfect canvas for subtle color play. Tinted or frosted acrylic adds vibrancy without overwhelming neutral interiors.
Use pastel-tinted acrylic panels in homes or frosted blue holders in minimalist offices. Colored acrylic sheets are available in over 40 hues, including translucent, opaque, and mirrored finishes.
02. Integrate Lighting
LED integration transforms acrylic into a glowing centerpiece. The idea is perfect for signage, awards, or ambient décor. Edge-lit acrylic signs use embedded LEDs to illuminate engraved text or logos.
Such a collaboration creates a floating glow effect. Use warm white LEDs for cozy environments and cool tones for tech-forward or gallery spaces.

03. Play with Shapes and Layers
Layering acrylic sheets or using geometric cuts adds dimensionality and visual intrigue. Stack clear and frosted layers with offset shapes to create depth in wall art or signage.
Retail stores use hexagonal acrylic panels layered in honeycomb patterns to display accessories. Laser cutting enables precision shaping of acrylic into circles, triangles, waves, and custom silhouettes.
04. Combine Materials
Acrylic pairs beautifully with natural and industrial materials. It creates a balanced and contemporary aesthetic. Wood adds warmth, metal introduces edge, and greenery softens the look.
Acrylic shelves are mounted on reclaimed wood backdrops with embedded succulents. Use brushed brass with clear acrylic for luxury, or matte black metal with frosted acrylic for minimalism.
05. Personalized Engraving
Laser engraving allows for intricate personalization – logos, quotes, patterns, or even illustrations. Consider custom nameplates, wedding signage, branded awards, or inspirational wall panels.
Laser engraving on acrylic produces polished, permanent etching without ink or wear over time. Combine engraving with edge lighting to make quotes/logos glow (reception desks or gallery walls).
Placement and Styling Tips for Maximum Impact
The ultimate goal is to make your space, brand, or products glow enough to grab attention. That’s where strategic placement and styling of acrylic displays come into mind.
a. Eye-Level Placement
Positioning acrylic displays at eye level naturally captures attention and encourages interaction. In retail, eye-level placement increases product visibility and impulse purchases by up to 35%.
Use eye-level acrylic frames for menus in cafés or promotional inserts at reception desks to maximize readability and engagement.
b. Highlight Key Items
Acrylic displays work best when used to spotlight premium or priority items. It turns them into visual focal points.
Use tiered acrylic stands or illuminated signage to draw attention to bestsellers, new arrivals, or limited-time offers.
c. Keep It Minimalist
Acrylic thrives in minimalist setups. Overcrowding reduces impact and creates visual noise. Allow for negative space around each display to enhance clarity and sophistication. Minimalist displays are associated with higher perceived value and better brand recall.

d. Optimize Lighting
Acrylic’s reflective surface amplifies ambient and direct light, making it ideal for brightening dim areas. Use spotlights or LED strips to create glowing edges or highlight engraved elements.
Position acrylic near natural light sources or use warm LEDs to soften the glow against harsh reflections.
e. Coordinate with Brand or Room Theme
Styling acrylic displays to match your brand identity or interior theme ensures cohesion and professionalism. Align acrylic color tints, typography, and layout with your brand palette or room décor.
Consistent visual branding across displays can improve customer trust and recognition by up to 80%. For events, match acrylic signage with floral arrangements or table linens to create a unified aesthetic.
Choosing the Right Acrylic Display for Your Needs
01. Purpose Identification: Decorative, Promotional, or Functional
- Decorative: Opt for engraved panels, illuminated signs, or artistic shapes for homes, weddings, or galleries.
- Promotional: Use tiered stands, sign holders, or branded podiums to highlight products and offers in retail or events.
- Functional: Offices, hospitality, or service desks benefit from brochure holders, nameplates, and organizational tools.
02. Size and Space Considerations
Choosing the right size ensures your display complements the environment without overwhelming it.
- Small Spaces: Use compact tabletop displays or wall-mounted shelves.
- Large Venues: Opt for freestanding acrylic towers, illuminated signage, or multi-tiered stands.
- Proportional Design: A display that’s too small may go unnoticed; too large can disrupt flow and aesthetics.

03. Customization Options: Branding, Shape, and Color
- Branding: Laser engraving, UV printing, and logo-shaped cutouts.
- Shape: Geometric, organic, or thematic silhouettes.
- Color: Clear, frosted, tinted, mirrored, or LED-integrated options.
04. Budget and Quality Balance
Acrylic displays range from budget-friendly to premium-grade. The key is balancing durability with cost.
- Low Budget: Opt for standard clear acrylic with basic cuts.
- Mid-Range: Choose anti-scratch finishes and modular designs.
- High-End: Invest in thick, polished acrylic with lighting and engraving.
05. Supplier Credibility
What to Look For: CNC-cutting capabilities, UV printing, anti-yellowing guarantees, and global client portfolios.
Suppliers like Jumei serve international brands, offering modular, transport-friendly designs for trade shows and retail chains.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1) How can acrylic displays enhance my space?
Acrylic displays add elegance, improve product visibility, and create a modern, clutter-free aesthetic. They’re ideal for organizing, promoting, or decorating any environment.
2) What types of acrylic displays are best for retail stores?
Retail stores benefit from acrylic risers, tiered stands, sign holders, and display boxes. These highlight products while maintaining a clean, professional look.
3) Are acrylic displays suitable for weddings and events?
Yes. Acrylic is widely used for weddings and events in the form of table numbers, welcome signs, seating charts, and centerpieces. It adds a modern, elegant touch to any theme.
4) Can I customize acrylic displays with my logo or design?
Absolutely. Acrylic can be laser-engraved, UV-printed, or cut into custom shapes. You can include logos, quotes, or patterns for branding or personalization.
5) What’s the difference between clear, frosted, and colored acrylic?
Clear acrylic offers maximum transparency, frosted acrylic provides a soft matte finish, and colored acrylic adds visual interest. Each serves different aesthetic and functional purposes.
6) Are acrylic displays durable for outdoor use?
Yes. High-quality acrylic is UV-resistant and weather-tolerant. They’re particularly suitable for outdoor signage, display cases, and event décor.
7) How do I clean and maintain acrylic displays?
Use a microfiber cloth and mild soap solution to keep things clean. Avoid ammonia-based cleaners, which can cause clouding or scratches.

Conclusion
Acrylic displays hold elegance, versatility, and impact. Its crystal-clear beauty, customizable design, and functional strength make it perfect for storytelling, branding, and transformation. A creative styling unlocks the power to elevate any space – visually, emotionally, and experientially.
Redefine Your Space through Creative Acrylic Displays with JUMEI
Shape your creative designs in acrylics with captivating options from Jumei Acrylic. We specialize in acrylics as all our products feature top-tier designs. Check the stock and contact us about the services.
]]>No matter the case, how your brand is presented directly influences consumer perception, engagement, and buying behavior. Discover acrylic display stands to turn a casual glance into a lasting impression.
What Makes Acrylic Display Stands Good for Visibility?
· Crystal-Clear Transparency
Acrylic’s optical clarity rivals glass without the fragility. Its 92% light transmission rate ensures products are visible from every angle. Such clarity brings life to acrylic elements to showcase fine details in jewelry, cosmetics, tech gadgets, or food items.
You can get up to 94% clarity with Jumei’s acrylics. Such an unobstructed view enhances perceived value. Consumers are more likely to trust and engage with products they can see. Transparent displays can increase product interaction by up to 40%.
· Professional and Aesthetic Appeal
Acrylic stands feature a sleek and minimalist aesthetic that complements any brand identity. The material and its designs go well with rustic to futuristic brands. The clean lines and polished surfaces are favored in luxury boutiques, tech showrooms, and fashion exhibitions.
Your presentation is likely to reflect premium quality, especially for high-end brands. Apple, for instance, incorporates acrylic risers in its stores to elevate accessories without distracting from the product itself. Such a subtle elegance reinforces brand credibility and consumer trust.

· Durability and Reusability
Unlike glass, acrylic is shatter-resistant and 17 times stronger. That’s why it’s ideal for high-traffic environments like trade shows or retail floors. The durable material can withstand wear and tear, UV exposure, and temperature fluctuations with proper care.
Compared to cardboard or wood, which degrade quickly, acrylic stands can be reused across multiple campaigns. It reduces waste and replacement costs. Many global retailers report saving up to 30% annually by switching to reusable acrylic fixtures.
· Lightweight and Portable (Drill Holes)
Despite its magnificent strength, acrylic remains easy to handle. A beneficial strength-to-weight ratio is perfect for mobile setups, seasonal promotions, or pop-up events. Exhibition teams prefer acrylic for its quick setup and rearrangement flexibility.
Such setups feel like a straightforward fix with frequent booth layout changes. A single person can transport and install multiple stands without specialized equipment. Therefore, you can expect streamlined logistics and reduced labor costs.
· High Customization Potential
Acrylic’s versatility enables the manufacturing of custom shapes, sizes, and finishes. Brands can engrave logos, apply UV printing, or mold stands into thematic designs. For instance, you can go for wave-shaped risers for beachwear or geometric tiers for tech gadgets.
Color tinting and LED integration can further add visual drama, especially in dim environments like nightclubs or gallery spaces. Such a simple customization can transform functional stands into branded storytelling tools that can enhance emotional engagement.
· Cost-Effective Marketing Investment
The upfront cost for acrylic stands may seem higher than cardboard or plastic. However, acrylic’s long lifespan and superior reusability make it a smart investment. Businesses save on frequent replacements and elaborate decor setups.
Moreover, acrylic’s ability to elevate presentation means higher perceived product value towards increased sales. Acrylic stands offer one of the highest ROI rates among display materials for small and medium-sized retailers.
Different Types of Acrylic Display Stands
Weather-resistant acrylic stands come in diverse standoff options to suit specific settings. Each design tool with full color can maximize visibility, engagement, and brand impact at particular setups.
01. Countertop Display Stands
These strategic stands are perfect for showcasing small but high-margin items like cosmetics, accessories, and tech gadgets. Positioned near checkout counters, they capitalize on impulse buying behavior.
Brands like Sephora and Apple use sleek acrylic risers to highlight new arrivals or limited-time offers. Use tiered countertop designs with clear labeling and LED accents to guide customer focus and increase conversion.
02. Floor Standing Acrylic Displays
These freestanding units are ideal for larger products, directional signage, or promotional visuals. Commonly seen in malls, showrooms, and exhibitions, they offer high visibility from a distance.
You can customize the design with shelving, hooks, or poster frames. For example, tech expos often use floor acrylic towers to present tablets or VR gear in a clean, futuristic format.

03. Tiered and Multi-Level Stands
Tiered acrylic stands allow vertical product stacking, maximizing space while maintaining visibility. They’re especially popular for jewelry, pastries, perfumes, and collectibles, where showcasing multiple items without overlap is key.
Bakeries in Tokyo and Paris often use multi-level acrylic trays to present macarons and desserts, enhancing visual appeal and hygiene. Tiered displays can increase product exposure by up to 35% in compact retail environments.
04. Rotating Acrylic Stands
Adding motion and interactivity, rotating stands are excellent for brochures, sunglasses, keychains, or small accessories. They encourage browsing and tactile engagement, which can boost dwell time and sales.
Travel agencies and bookstores frequently use rotating towers to organize flyers or postcards in an engaging format. Combine rotation with clear category labeling to guide customer exploration and reduce decision fatigue.

05. Acrylic Sign Holders
They display menus, price lists, promotional messages, or directional signage. Acrylic sign holders come in table-top, wall-mounted, and hanging formats.
Restaurants, salons, and trade booths rely on them for professional communication. The transparency ensures the message is the focus, while its durability withstands frequent updates.
06. Custom Acrylic Signs
They’re tailored to reflect brand identity, featuring logos, color contrast, engraved messaging, or integrated lighting. Used at product launches, corporate events, and exhibitions, they create immersive brand experiences.
For instance, luxury watch brands often use branded acrylic pedestals with spotlighting to evoke exclusivity and craftsmanship. Custom branding on display stands can increase brand recall by up to 70% at events and expos.

Acrylic Display Stands or Plexiglass Signs for Different Occasions
Acrylic display stands can be transformative art tools or a background screen for installation. You can order a particular quantity simultaneously to enhance visibility, elegance, and brand storytelling.
a. Retail Environments
In retail, first impressions drive conversions. Acrylic display stands are ideal for –
- Showcasing new arrivals, premium products, or limited-time offers at eye level, especially near entrances or checkout counters.
- Maintaining brand consistency with sleek, transparent designs that don’t distract from the product. Their neutrality complements any color palette or store theme.
b. Trade Shows and Exhibitions
Trade shows demand portable, professional, and eye-catching displays. Acrylic stands deliver –
- Lightweight, modular solutions that are easy to transport and assemble.
- Highlighted products, brochures, or digital signage in an organized manner.

c. Corporate Offices and Reception Areas
Acrylic displays add a touch of sophistication and professionalism to corporate settings. They’re –
- Award showcases, company mission statements, or branded signage in lobbies.
- Used to organize brochures, visitor guides, or event flyers in waiting areas.
d. Restaurants, Cafés, and Hotels
In hospitality, acrylic stands in balance functionality with aesthetic appeal. They’re –
- Used for menu holders, table numbers, reservation signs, or promotional displays.
- Smudge-resistant surfaces blend seamlessly with rustic, modern, or luxury interiors.
e. Events and Celebrations
From weddings to corporate galas, acrylic stands bring elegance and personalization. It seems –
- Ideal for welcome signs, seating charts, table numbers, or branded decor.
- Can be laser-cut, engraved, or tinted to match event themes and color palettes.
f. Museums and Galleries
In cultural spaces, acrylic stands serve both protective and aesthetic functions. They’re –
- Used to display artifacts, artwork, or informational plaques without overshadowing the exhibit.
- Acrylic’s optical clarity (up to 92% light transmission) ensures minimal visual interference.

Design and Placement Tips to Maximize Visibility
· Strategic Placement
Positioning is everything. Acrylic displays should be placed at eye level or in high-traffic zones to ensure maximum exposure.
Eye-level placement aligns with natural sightlines, making products more noticeable and accessible.
In trade shows or exhibitions, position acrylic stands near booth entrances or along customer flow paths to capture attention early.
· Use Lighting to Your Advantage
Lighting transforms acrylic from functional to captivating. LED integration or spotlighting enhances clarity, adds drama, and draws focus to featured items.
Effective LED placement in acrylic stands improves product visibility and customer engagement while maintaining energy efficiency.
Luxury brands in Dubai and Tokyo often use backlit acrylic risers to showcase jewelry or tech gadgets, creating a premium ambiance that encourages closer inspection.
· Keep Displays Clean and Scratch-Free
Acrylic’s brilliance depends on maintenance. Dust, fingerprints, and scratches can dull its clarity and reduce perceived product value.
Regular cleaning with microfiber cloths and non-abrasive cleaners preserves its professional look.
Clean and well-maintained displays increase customer trust and dwell time by 20%, especially in high-end retail.

· Create a Focal Point
Use acrylic stands to anchor visual attention. Highlight hero products, limited editions, or promotional items by placing them on elevated or uniquely shaped acrylic platforms.
It creates a natural focal point that guides the customer’s gaze. Combine focal acrylic stands with complementary signage or lighting to reinforce product importance and storytelling.
· Maintain Visual Balance
Clutter kills clarity. Acrylic displays should be arranged to allow products to “breathe” visually, avoiding overcrowding.
It enhances focus and reduces cognitive overload, making it easier for customers to process and appreciate each item.
Sunday Knight recommends using odd-numbered groupings and spacing items evenly to maintain aesthetic harmony.
· Customize for Branding
Acrylic’s versatility allows for subtle branding enhancements. Add logo etching, brand colors, or custom shapes to reinforce identity without overwhelming the product.
It is especially effective in corporate events, product launches, and branded pop-ups. Custom-branded displays can increase brand recall by up to 70%.
Maintenance and Care Tips
Acrylic display stands require regular cleaning, proper handling, and strategic storage. Otherwise, it becomes difficult to retain the visibility.
a. Clean with Gentle Solutions
Acrylic is prone to scratching and clouding if cleaned improperly. Experts recommend using mild soap and lukewarm water.
Never apply ammonia-based cleaners, which can cause hazing or micro-cracks. A soft microfiber cloth is ideal for wiping surfaces without leaving streaks or abrasions.
Avoid paper towels or rough fabrics, which can scratch the surface. Use circular motions when cleaning to maintain optical clarity.
b. Regular Dusting and Polishing
Dust accumulation dulls acrylic’s shine and reduces visibility. Weekly dusting with a dry microfiber cloth keeps surfaces clean.
Get acrylic-safe polish to restore clarity and remove fine scratches on retail windows under direct sunlight.
Polishing compounds like Novus or Plexus are widely used in retail and gallery settings. Buffing with a soft pad can rejuvenate older stands.

c. Store Properly When Not in Use
Improper storage can lead to scratches, cracks, or warping. Always store acrylic stands in cool, dry environments, preferably wrapped in soft cloth or bubble wrap.
Stack vertically with padding between units. Avoid placing heavy items on top of acrylic surfaces. Label storage boxes with stand types and dimensions to streamline setup.
d. Treat Stains and Scratches Promptly
Stains from adhesives, oils, or food should be cleaned immediately to prevent permanent damage. For scratches, use fine-grit sandpaper followed by polish for deeper marks. Apply acrylic scratch removers for surface-level blemishes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1) What are acrylic display stands used for?
Acrylic display stands are used to showcase products, signage, or promotional materials in retail stores, exhibitions, offices, and events. The transparency and sleek design enhance visibility and presentation.
2) Why are acrylic display stands better than glass or cardboard?
Acrylic is more durable, lightweight, and shatter-resistant than glass, and it lasts longer than cardboard. It offers crystal-clear visibility without compromising safety or longevity.
3) How do acrylic display stands improve product visibility?
Acrylic’s high light transmission (up to 92%) ensures unobstructed views from all angles. It can make products appear more attractive and accessible to customers.
4) Are acrylic display stands suitable for indoor and outdoor use?
Yes, but UV-resistant acrylic is recommended to prevent yellowing or warping. They seem ideal for outdoor signage, kiosks, or event branding.
5) How do I maintain acrylic display stands?
Clean regularly with mild soap and microfiber cloths. Avoid ammonia-based cleaners and store them in cool, dry places to prevent scratches and discoloration.
6) Can acrylic display stands be customized?
Absolutely. Acrylic can be laser-cut, engraved, color-tinted, or integrated with lighting and logos to match your brand identity and event theme.
7) What is the best placement for acrylic display stands?
Place stands at eye level or in high-traffic areas like entrances or checkout counters to maximize visibility and engagement.
8) Are acrylic stands reusable for multiple events?
Yes. Acrylic stands are durable and reusable, making them a cost-effective solution for trade shows, seasonal promotions, and recurring campaigns.
9) How do acrylic stands enhance branding?
Custom acrylic stands with logos, colors, and unique shapes reinforce brand identity and create a cohesive visual experience across touchpoints.
Conclusion
Brand visibility goes well beyond the idea of ‘being seen’ by emphasizing ‘being remembered’. Acrylic display stands offer a powerful blend of clarity, elegance, and adaptability. It can transform ordinary presentations into extraordinary brand experiences.
Maximize Your Visibility with Acrylic Displays from Jumei
Jumei Acrylic, a pioneer in modern acrylic manufacturing, is ready to push your visibility with top-tier designs. Contact us to know how our experience and innovation can coincide with your target.
]]>What are Special Thick Acrylic Sheets?
Special Thick Acrylic Sheets are, as the name suggests, solid acrylic panels with thicknesses far exceeding standard specifications. Our specialized range covers an impressive spectrum from 50mm to a monumental 200mm. These are not mere sheets, but solid “acrylic blocks.” This substantial thickness grants them physical properties that traditional acrylic or glass cannot match, making them the ultimate solution for extreme conditions and load-bearing applications.
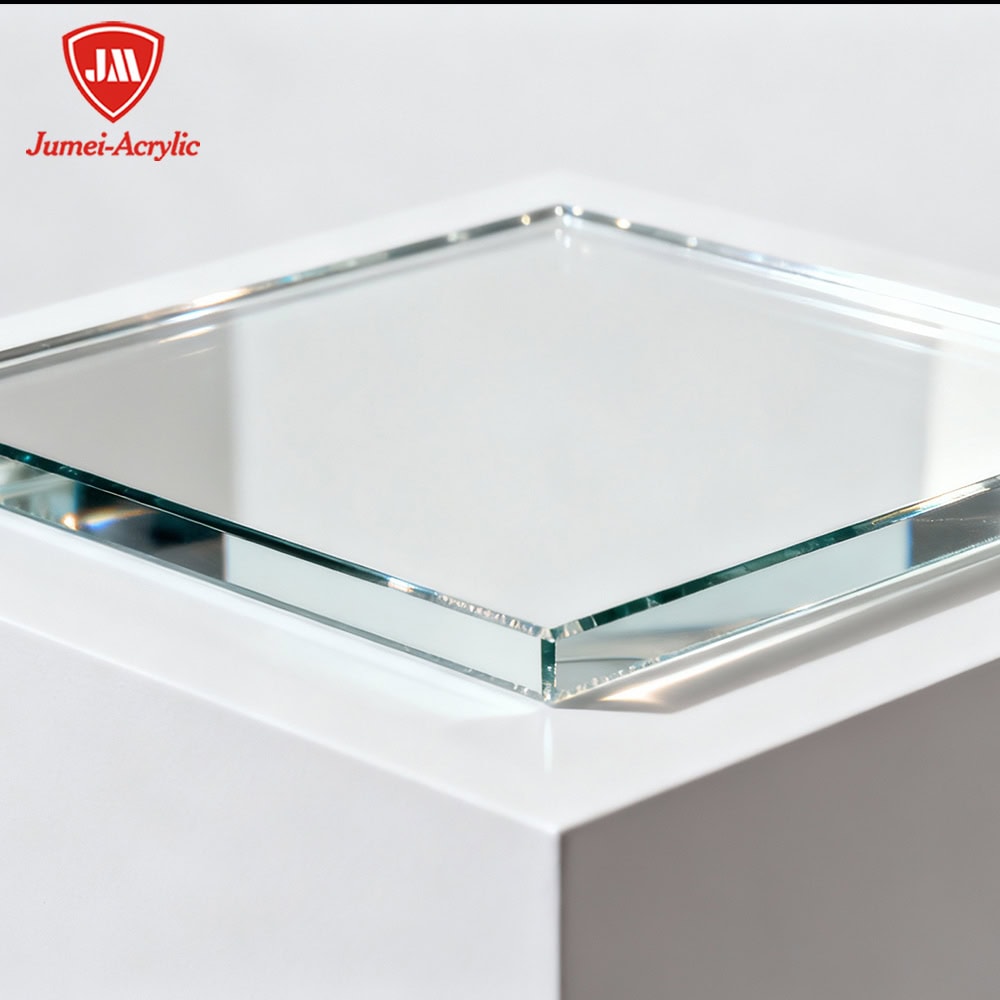
Top Benefits of Special Thick Acrylic Sheets
- Unmatched Impact Resistance & Durability
This is the core advantage of our special thick sheets. Their impact resistance is more than 10-20 times that of standard glass. Supported by their 50mm to 200mm thickness, they can withstand significant impact, heavy pressure, and continuous load. Whether it’s vandalism in public spaces or accidental falling objects, these sheets remain intact, providing supreme security. - Exceptional Load-Bearing Capacity
Common building materials often have limitations in span and load-bearing. Our thick acrylic sheets, with their massive thickness, can function as structural components. They support immense static and dynamic loads, meaning they can serve not only as protective barriers but also as part of a load-bearing platform, unlocking infinite design possibilities. - Crystal Clarity & Superior Weatherability
Despite their impressive thickness, these sheets retain the innate high transparency of acrylic material, with a light transmittance of up to 93%. Even at such thickness, the interior remains perfectly clear, without yellowing or hazing. They also boast powerful weatherability, resisting UV radiation and maintaining their crystal-clear appearance outdoors for years, without becoming brittle or discoloring like standard plastics. - Unrivaled Safety Features
When subjected to extreme force, special thick acrylic sheets do not shatter into dangerous fragments like glass. They either remain intact or may crack while still holding their structural integrity, significantly reducing the risk of injury to personnel and damage to property. This characteristic makes them the premier choice for locations with the highest safety requirements.
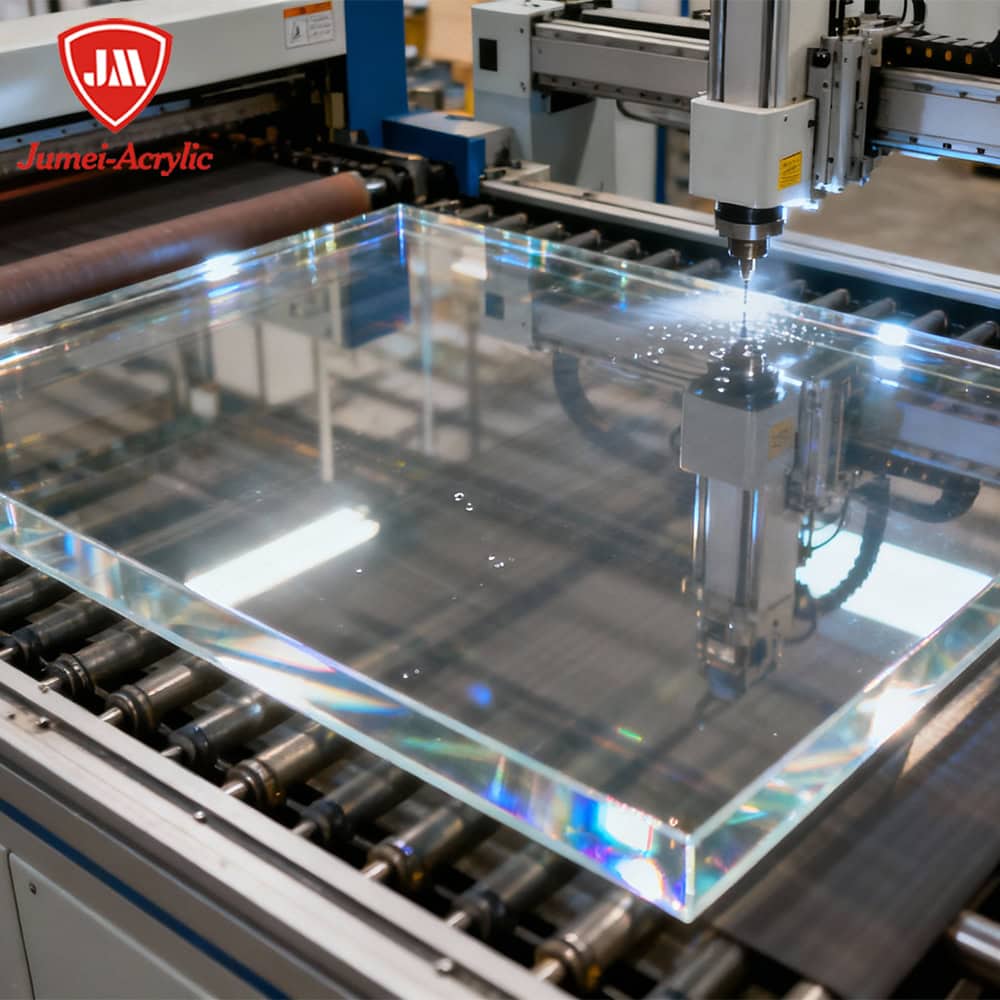
Revolutionary Applications for Special Thick Acrylic Sheets
Leveraging these benefits, our 50-200mm thick acrylic sheets are becoming indispensable in the following fields:
Infinity Pools & Observation Decks: Create stunning “transparent pool walls” or cliff-side viewing windows. Their immense thickness is designed to withstand the pressure of millions of liters of water while offering an unparalleled visual experience.

High-Strength Staircase Balustrades & Protective Barriers: In modern architecture, they are used to create extremely robust staircase handrails and floor partitions. They are not only safe and secure but their transparent nature maintains an open feel and allows free flow of light, perfectly blending safety with aesthetics.

Aquarium & Oceanarium Observation Panels: Ideal for large marine exhibit tanks or deep-sea observation tunnels, capable of withstanding enormous water pressure while presenting visitors with the clearest, most breathtaking view of the underwater world.
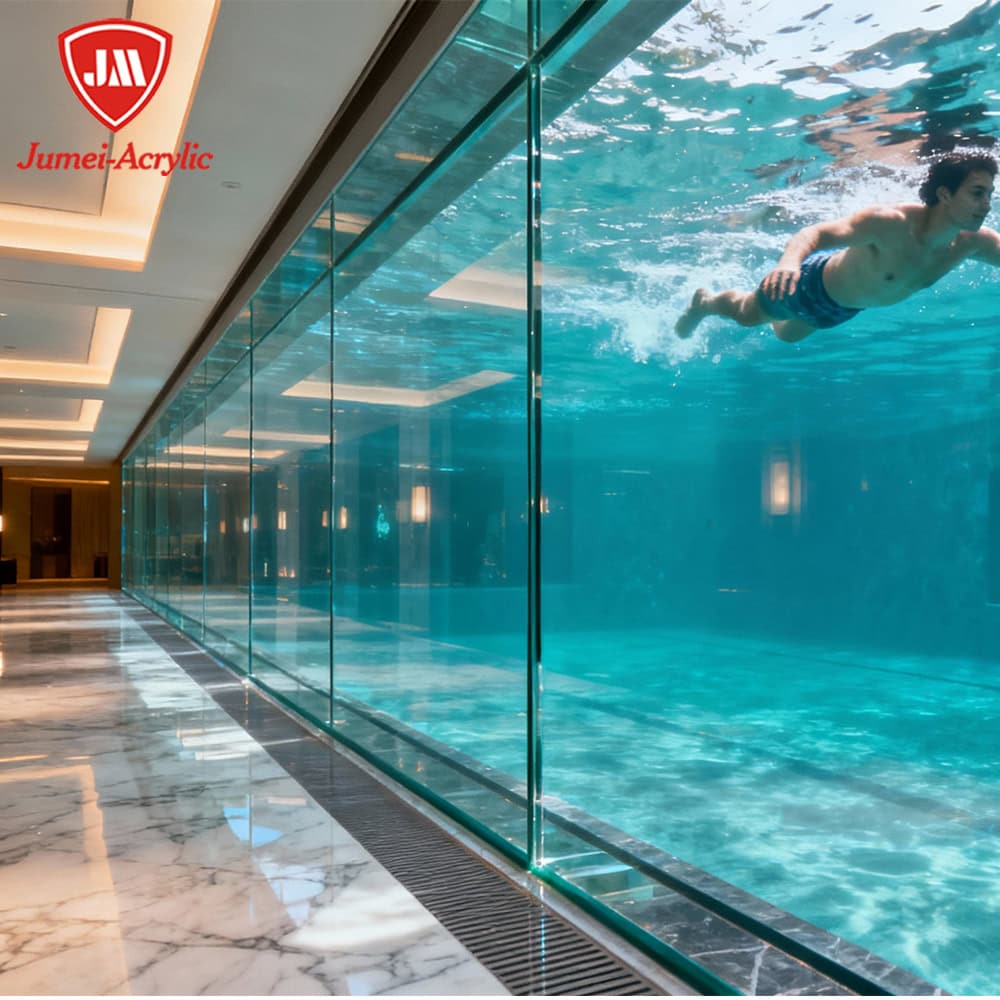

Why Choose Our Special Thick Acrylic Sheets?
Our special thick acrylic sheets are manufactured using top-grade cast cell technology, ensuring uniform molecular structure and optical properties from core to surface. This eliminates internal bubbles, impurities, or distortions that can occur with such thicknesses. Each panel is meticulously ground and polished, with edges as smooth as crystal, ensuring absolute safety during handling and installation.
Conclusion:
When your project demands the ultimate in strength, load-bearing capacity, and safety, conventional materials often fall short. Our Special Thick Acrylic Sheets (50-200mm) are engineered precisely for these challenges. They are more than just a material; they are a powerful engineering solution, enabling the safest and clearest realization of your most ambitious designs.
Contact us today to explore the limitless potential of special thick acrylic for your next landmark project!
]]>Display materials silently but surely hold your brand’s professionalism, quality, and attention to detail. Acrylic displays have emerged as a standout choice to combine visual appeal with practical functionality.
Why Acrylic Displays Are Ideal for Retail and Business Promotion?
Display options can range from traditional glass to flexible polycarbonate and other plastics. Nonetheless, acrylic or plexiglass remains on top to handle retail and business promotion.
a. Professional Aesthetics
Acrylic’s crystal-clear transparency is directly comparable to standard glass. However, the former comes with greater resilience. Even the clean, polished, and modern look enhances product visibility.
Such clarity can draw instant attention to the product rather than the display itself. You can showcase valuables like cosmetics, showpieces, consumer electronics, jewelry, and promotional materials.
Brand Compatibility: Acrylic complements diverse brand identities. Luxury boutiques now use polished acrylic risers. Meanwhile, tech startups leverage the material’s minimalist brochure holders.
Japan’s Muji stores extensively implemented plexiglass acrylic to reinforce their minimalist branding. Even the luxury retailers in Paris leveraged the advantages of frosted acrylic for elegant signage.
b. Durability and Longevity
Acrylic plexiglass is scratch-resistant and UV-stable from the start. It’s rather suitable for indoor and outdoor use. Even prolonged exposure to harshness can’t initiate yellowing and cracking over time.
Material Strength: Acrylic is 17x stronger than glass and weighs half as much, reducing breakage risk.
Always choose cast acrylic for premium durability and extruded acrylic for on-budget bulk displays.
c. Versatility for Retail Displays
Capable manufacturers can cut, bend, engrave, or print modern acrylic into any shape or design. Such versatility makes the thermoplastic perfect for custom branding, thematic displays, and modular setups.
You can literally ask for anything from the right manufacturers, like Jumei. Acrylic, when appropriately implemented, can deliver anything – laser-cut logo plaques, curved product stands, or tiered shelving.
Beauty retailers like Sephora rely on custom acrylic makeup organizers to streamline product access. The adoption of plexiglass sheets in this case set an example by reinforcing the brand’s aesthetics.

d. Cost-Effectiveness
Acrylic requires more initial investment for business needs than alternatives like metal, wood, or PVC objects. The durable material with low maintenance eventually justifies the cost for a fast turnaround.
Retailers can reduce up to 30% in display replacement costs over 5 years upon switching. Regular cleaning with microfiber cloths and mild soap keeps acrylic looking new without special treatments.
e. Lightweight and Portable
Acrylic’s lightweight nature enables easy handling, transportation, and installation. Mobile businesses, trade shows, and seasonal promotions have immensely benefited from lightweight acrylic sheets.
Acrylic signage and product holders have become the global standard for expos like CES and Ambiente. Modular frames (stackable and collapsible) simplify logistics for pop-up shops and traveling vendors.
f. Acrylic Sheet Customization
As mentioned, you can opt for different methods, from laser engraving to colored acrylic panels. And businesses can personalize displays to reflect their brand identity. Options include –
- Logo printing.
- Backlit acrylic signage.
- Colored or frosted finishes.
- Modular display systems.
Brands extensively choose gold-tinted acrylic for premium appeal across Dubai’s retail hubs. Meanwhile, eco-conscious brands in Scandinavia mostly go for recycled acrylic variants.
Different Acrylic Displays for Retail and Business Promotion
Even acrylic displays come in various forms. You can look into a particular option to enhance product visibility, brand messaging, and customer engagement.
01. Acrylic Sign Holders and Frames
Display menus, price tags, and promotional offers + directional signage in a professional format.
The designs are available in countertop, wall-mounted, and hanging styles. Such formats suit diverse retail layouts, from cafes and salons to tech stores.
Consider implementing double-sided holders in high-traffic areas to keep your brand visible.
Acrylic sign holders have been the norm across IKEA stores worldwide to label product sections clearly. The holding frames also highlight seasonal offers.
02. Acrylic Display Stands
Elevate featured or exclusive products to draw attention towards bestsellers or new arrivals.
Jewelry stores invest in tiered acrylic risers to showcase rings and watches. Meanwhile, electronics retailers highlight gadgets like smartwatches or earbuds.
High design flexibility makes them available in U-shapes, stair-step risers, and pedestal forms. Elevated displays can increase product interaction by up to 28%.

03. Acrylic Brochure and Literature Holders
Organize and present your flyers, catalogs, and/or leaflets in a tidy yet accessible way. It’s common in reception areas, trade shows, and retail counters.
Choose from single-pocket, multi-tiered, and rotating holders to accommodate different volumes.
Many hotels and tourism centers in Europe drill holes to install wall-mounted acrylic holders. They particularly hold and display multilingual brochures.
04. Acrylic Display Boxes and Cases
Protect your valuable or fragile items on display while maintaining complete visibility.
Luxury retail (watches, perfumes), museums (for artifacts), and boutiques (for collectibles) heavily leverage the feature. Lockable lids + UV-resistant acrylic protect against theft and fading.
Install mirrored bases and/or LED-lit cases to enhance the overall visual appeal.
05. Acrylic Wall Displays
Showcase artwork, certificates, or branded visuals in a sleek, modern, and catchy format.
Such displays add a clean, steady, and frameless aesthetic to office walls, galleries, or retail interiors. Available options include standoff mounts, magnetic closures, and frosted finishes.
Silicon Valley companies use acrylic wall panels for innovation awards and brand milestones.
06. Acrylic Countertop Displays
Strategically place the countertop display near checkout counters to encourage impulse purchases.
It serves small yet high-margin items (lip balms, phone accessories, or gift cards) well. Available design tool options include bins, tiered trays, and rotating carousels.
Retail Dive reports that impulse buys can account for 20% – 30% of total sales in many retail sectors.
07. Custom Acrylic Signs / Displays
Customize your flexible displays aligned with brand identity and promotional goals. Customization options include –
- Logo-shaped holders.
- Tiered racks with brand colors.
- Backlit or LED-illuminated signage.
Consistent visual identity across displays reinforces brand recognition and trust.
Nike flagship stores have custom acrylic sneaker pedestals with embedded lighting and branding. Such custom designs induce immersive product experiences.

Best Practices for Using Acrylic Displays Effectively
Maximizing the impact of acrylic displays in retail and business settings isn’t exactly straightforward. Brands must adopt some strategies to make the most out of the investment.
a. Match Display Design with Brand Aesthetic
Consistency remains mandatory in visual merchandising. Acrylic displays should reflect your brand’s tone. It’s the same for minimalist, luxurious, playful, or tech-forward ones.
Consider colored acrylic or inserts that match your brand palette. Go for subtle logo etching or UV-printed branding on displays to reinforce identity.
The display lighting should complement your project’s or store’s ambiance. For example, warm tones go well with cozy boutiques, whereas cool tones suit tech or wellness brands.
Modular acrylic units can be rearranged while maintaining brand consistency. Such an approach retains the ambiance throughout seasons or campaigns.
b. Keep Plexiglass Signs Clean and Polished
Acrylic’s glass-like clarity has been one of the most pioneering strengths. However, the transparency also marks its most significant vulnerability.
- Maintenance routine: Clean with a microfiber cloth and non-abrasive cleaner to avoid scratches.
- Avoid ammonia-based products: Those cleaning chemicals cause clouding or micro-cracks over time.
A well-maintained display can increase perceived product value by up to 25%. Assign daily wipe-downs as part of staff closing routines.

c. Highlight Key Products
Use acrylic displays to spotlight high-margin, seasonal, or new products strategically.
- Tiered risers: Elevate your bestselling products to eye level.
- Sign holders: Pair with promotional messaging to drive urgency.
Sephora uses acrylic trays and risers to feature new arrivals at the front of the store. Products placed in acrylic risers near eye level see up to 40% more engagement.
d. Optimize Lighting for POP Displays
Lighting transforms acrylic from functional to visually magnetic.
- Backlighting: Grabs the client’s attention to signage or product features.
- LED strips: Embedded in display edges to deliver a futuristic glow.
Match the lighting temperature to the store’s mood, like warm white for fashion. South Korean flagship cosmetic stores have LED-lit acrylic displays to create immersive product zones.
e. Rotate Displays Regularly
Stale displays lead to visual fatigue. Keep things fresh to encourage repeat visits.
- Seasonal updates: Swap out inserts, signage, or featured products monthly or quarterly.
- Event tie-ins: Align your displays with holidays, product launches, and/or local events.
Studies show that rotating displays every 30 days can boost foot traffic by 20%. Modular acrylic systems enable quick reconfiguration without full replacements.
f. Choose Quality Materials
Not all acrylic is created equal. Cheap variants may yellow, crack, or warp, which can damage your brand image. Look for –
- UV-resistant acrylic for sunlit areas.
- Cast acrylic for premium clarity and strength.
- Scratch-resistant coatings for high-traffic zones.
Investing in quality materials reduces replacement frequency and enhances brand perception. Premium-grade acrylic can last 5 – 10 years with proper care.
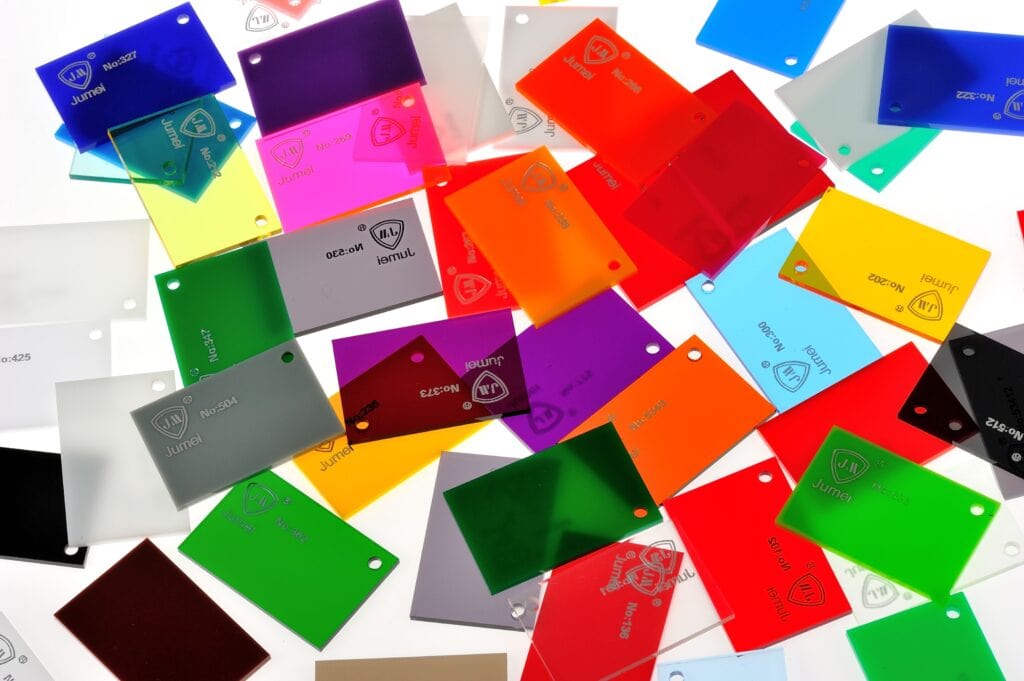

Examples and Applications of Acrylic Displays
01. Retail Stores
Jewelry / Eyewear: Tiered acrylic risers and velvet-lined acrylic trays.
Cosmetics: Clear acrylic organizers to group lipsticks, palettes, and testers.
Electronics: Acrylic stands to elevate phones and tablets with embedded lighting.
02. Restaurants and Cafés
Menu Holders: Tabletop acrylic frames to display menus, daily specials, or QR codes.
Feedback Forms: Clear acrylic boxes with slotted lids encourage customer feedback.
03. Corporate Offices
Branded Signage: Wall-mounted acrylic plaques with standoff mounts.
Awards / Recognition: Custom-engraved acrylic trophies and certificates.
Literature Holders: Multi-tiered acrylic brochure holders for profiles, catalogs, or guides.
04. Trade Shows and Exhibitions
Product Displays: Clear risers and cases allow attendees to view products from all angles.
Brochure Stands: Freestanding holders keep promotional materials organized and accessible.
05. Boutiques and Salons
Product Pedestals: Highlight luxury skincare, fragrances, or haircare products with illuminated acrylic stands.
Countertop Displays: Small acrylic bins or trays near checkout areas encourage impulse purchases of accessories.

How to Choose the Right Acrylic Display for Your Business?
a. Assess Display Purpose
You must define the primary function of your acrylic display. It can be –
Promotional: Get tiered risers, countertop bins, or illuminated stands to spotlight new arrivals or seasonal offers.
Informational: Choose sign holders, brochure racks, or wall-mounted frames to share menus, product specs, or brand messaging.
Protective: Get enclosed acrylic boxes or lockable cases for high-value items like jewelry, electronics, or collectibles.
b. Consider Product Size and Weight
Acrylic displays must be proportionate and stable to support your products safely. For instance,
Light items: Lipsticks, brochures, or sunglasses work well with thin acrylic trays or holders.
Heavy items: Use thicker acrylic (≥5mm) for electronics, awards, or stacked merchandise.
Balance and safety: Base width and weight distribution prevent tipping in high-traffic areas.
Standoff options may reduce the shipping cost and save time within reasonable business days.
c. Evaluate Location: Indoor vs Outdoor
Your display’s environment affects material choice and design.
Indoor: Acrylic works well in climate-controlled spaces like boutiques or office settings.
Outdoor: Use UV-resistant acrylic to prevent yellowing / warping under direct sunlight.
Permanent setups: Wall-mounted or bolted displays offer stability and branding permanence.
Portable setups: Lightweight, modular acrylic stands are ideal for trade shows or pop-ups.

d. Customization for Clear Acrylic
Customization enhances brand recognition and customer engagement. Therefore,
Branding: Laser engraving, screen printing, or vinyl overlays for logos and taglines.
Full Color tinting: Use frosted, gold, or colored acrylic to match aesthetics or seasonal themes.
Lighting: Integrate LED strips or backlighting to add depth and visibility in dim conditions.
e. Supplier Quality and Reviews
Partnering with a reliable manufacturer ensures durability and long-term ROI. You should keep up –
Check reviews: Look for testimonials, case studies, and ratings from other businesses.
Material specs: Confirm premium-grade acrylic (Lucite, Perspex) and quality control standards.
Pioneering suppliers like Jumei Acrylic serve international clients with tailored solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are acrylic displays, and why are they popular in retail?
Acrylic displays are transparent fixtures made from durable PMMA to showcase products, signage, or literature. A sleek look, versatility, and affordability make them ideal for retail environments.
2. Are acrylic displays suitable for outdoor use?
Yes, when the acrylic is made from UV-resistant, weather-resistant acrylic. Such variants can actively resist yellowing and cracking, making them ideal for outdoor signage, kiosks, and promotional stands.
3. How do acrylic displays improve customer engagement?
Acrylic elevates product visibility by creating an organized layout that customers easily find and interact with featured items.
4. Can acrylic displays be customized for branding?
Absolutely. Businesses can add logos, color tinting, laser engraving, or LED lighting to match the brand’s aesthetic appeal and reinforce identity.
5. Are acrylic displays eco-friendly or recyclable?
Acrylic is recyclable, though not biodegradable. Some manufacturers have recycled options, making it a more sustainable choice for eco-conscious brands.
Conclusion
Acrylic displays offer the perfect blend of elegance, durability, and strategic impact. You can showcase premium products, guide customer decisions, or reinforce brand identity. Acrylic displays adapt to your goals, amplify your message, and create first impressions to convert observers into buyers.
Perfect Retail Business Displays with Fast Delivery from JUMEI
Start outrunning your direct competitors with eye-catching displays from Jumei Acrylic. We specialize in acrylics as all our products feature top-tier designs. Check the stock and contact us about the services.
]]>They may look similar at first glance, but they start to differentiate in their manufacturing processes. And such distinction continues with separate performance, cost, and suitability for specific applications.
What is Cast Acrylic?
It’s a premium-grade sheet formed through a meticulous process. Cast acrylic is made by pouring liquid methyl methacrylate (MMA) monomer between two highly polished glass plates.
The liquid is then polymerized, a chemical reaction that transforms it into a solid thermoplastic sheet. The result is a rigid material with excellent hardness, optical properties, and resistance.
Manufacturing Process of Cast Acrylic
- Preparation of the Mold: Two flat glass plates form the top and bottom surfaces of the sheet. A gasket or spacer is placed around the edges to define the sheet’s thickness.
- Pouring the Monomer: Liquid MMA monomer is mixed with initiators + additives and poured into the mold cavity. It’s done in a controlled environment to prevent contamination.
- Polymerization (Curing): The filled mold is placed in a temperature-controlled oven. It takes 8 to 24 hours, depending on sheet thickness, where the temp is gradually increased.
- Cooling and Demolding: The mold is slowly cooled to room temperature. The glass (good electrical conductivity) plates are removed, and the solid acrylic sheet is extracted.
- Finishing: The sheet edges may be trimmed, polished, or annealed (heat-treated) to improve mechanical stability. Cast acrylic sheets often have better thickness tolerance for CNC.

Characteristics of Cast Acrylic Sheets
01. Superior Optical Clarity: It’s renowned for great transparency. 92% transmission rivals glass while being half the weight with further impact resistance.
02. Minimal Distortion: Cast acrylic maintains clarity even when laser-cut or machined. That’s why it’s ideal for precision displays, museum cases, and high-end signage.
03. Thickness Variety: Cast acrylic can be manufactured in thicker sheets, ranging from 1.5 mm to 50 mm. Advanced techs can accomplish even up to 2 inches (50.8 mm) or more.
04. Dimensional Stability: Cast acrylic maintains consistent thickness across the sheet, with minimal internal stress. It can undergo CNC machining, laser engraving, and thermoforming.
05. UV Stability: No more yellowing and degradation even after 10+ years of sun exposure. High molecular weight comes with the ability to incorporate UV stabilizers.
06. Weather Resilience: It maintains its gloss and structural integrity in harsh climates, whether it’s tropical humidity, desert heat, or freezing conditions.
07. Polishability: The surface can be flame-polished or buffed to restore clarity after machining or wear.
08. Scratch Resistance: While not as hard as glass, cast acrylic is more scratch-resistant than extruded acrylic and can be coated for added protection.
Advantages of Cast Acrylic
a. No internal stress: Cast sheets have minimal internal stress, which means they maintain clarity even after laser cutting or CNC machining.
b. Ideal for premium displays: Luxury retail brands, museum exhibits, and high-end signage often use cast acrylic to ensure crisp visibility and a polished aesthetic.
c. Impact strength: While not as tough as a polycarbonate sheet, cast acrylic is significantly more impact-resistant than glass and maintains structural integrity under stress.
d. Weather resilience: It performs reliably in extreme temperatures, humidity, and pollution. It’s ideal for outdoor signage, architectural glazing, and solar panel covers.
e. Easy to Fabricate: Cast acrylic is a fabricator’s dream. Its low internal stress and consistent density ease cut, engrave, drill, and thermoform with precision.
Disadvantages of Cast Acrylic
i. Higher Cost: Cast acrylic is somewhat expensive, and in some cases, the price difference exceeds the standard threshold. Such a premium stems from a batch-based production process.
ii. Heavier Weight in Thicker Gauges: Cast acrylic’s density and structural integrity seem heavier in thicker formats. Cast sheets are produced in gauges up to 50 mm or more, adding substantial weight.
iii. Handling challenges: Thicker cast sheets require reinforced mounting systems, more labor during installation, and higher shipping costs.
iv. Design constraints: In weight-sensitive applications like suspended signage, portable displays, or drone-mounted components, cast acrylic may be impractical.
What is Extruded Acrylic?
It’s known for cost-efficiency, consistent thickness, and ease of mass production. Extruded acrylic is produced by forcing melted resin (typically PMMA pellets) through a precisely shaped die or mold.
Manufacturing Process of Extruded Acrylic
- Feeding Pellets: Raw plexiglass pellets (PMMA) are fed into a hopper, which channels them into a heated barrel. They’re pre-treated with additives, which may vary depending on desired sheet properties.
- Melting and Mixing: Inside the barrel, the pellets are heated between 180°C and 250°C, melting into a viscous liquid. Rotating screws mix the molten resin to ensure uniformity and remove air bubbles.
- Extrusion Through a Die: The molten acrylic is forced through a flat die, which shapes it into a sheet of specific thickness. The die can be adjusted to produce sheets ranging from 1mm to 10mm thick.
- Calendering and Cooling: The sheet passes through a series of calender rollers, which flatten and cool the material. These rollers may also impart texture or gloss based on the intended application.
- Cutting and Finishing: Once cooled, the sheet is trimmed to standard dimensions (4 x 8 or larger) for packaging. Some may be masked with protective film to prevent scratching during transport.
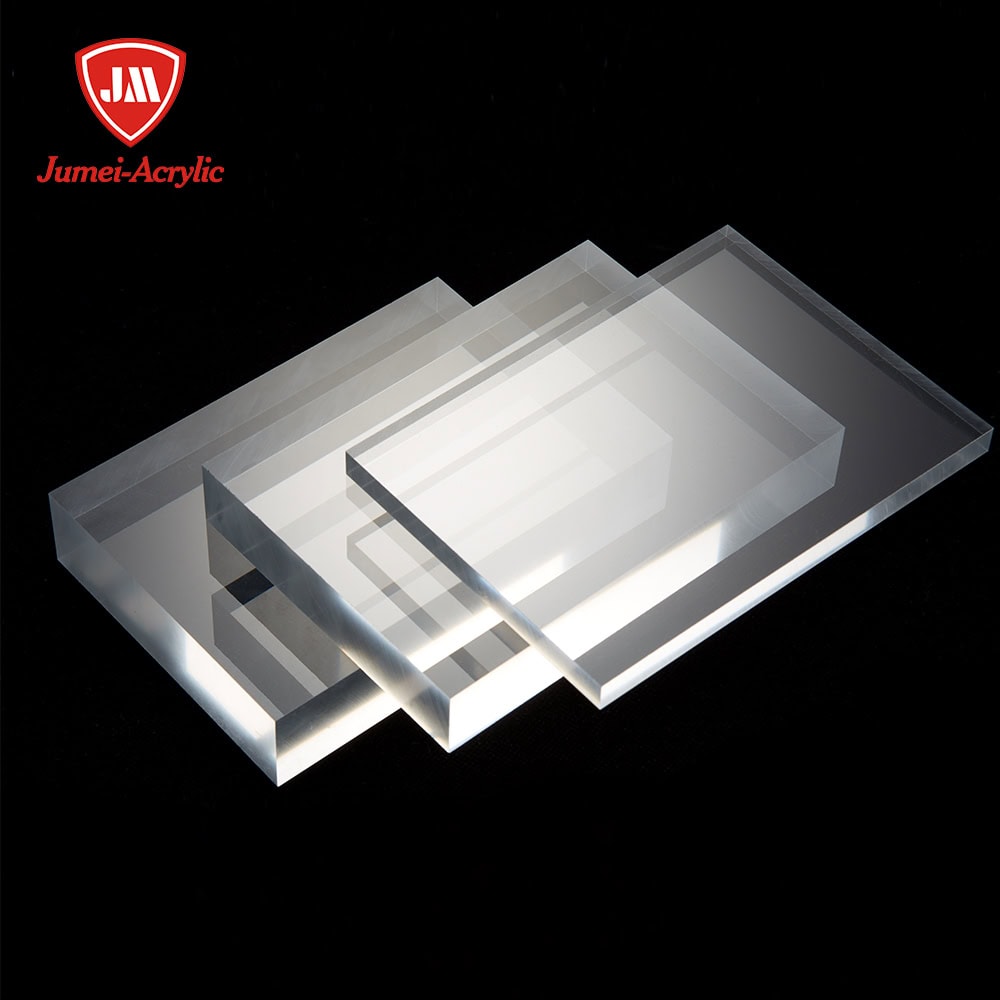
Characteristics of Extruded Acrylic Plastic
01. Uniform appearance: Extruded sheets often have a more uniform look due to their continuous production. But they may show minor flow lines or internal stress under polarized light.
02. Visual trade-off: While suitable for general signage and protective covers, extruded acrylic may not be ideal for luxury displays, aquariums, or optical-grade applications.
03. Bendability: Ideal for curved surfaces, protective shields, and lightweight display structures.
04. Standard sizing: Most extruded sheets come in 4′ x 8′ (1220 mm x 2440 mm) formats, optimized for cutting and fabrication.
05. Surface uniformity: The calendering process during extrusion ensures a smooth surface, but it may lack the depth and polish of cast sheets.
06. Scratch sensitivity: Slightly more prone to surface scratching due to lower hardness, though protective masking films are often applied during transport and handling.
Advantages of Extruded Acrylic
a. Typical savings: Extruded acrylic is generally 20% – 30% cheaper than cast acrylic. For bulk orders, this can translate into thousands of dollars in savings.
b. Scalable production: Manufacturers can run extrusion lines 24/7, producing over 10,000 kg of sheet material per week, which drives down unit costs.
c. Thickness tolerance: Extruded sheets typically maintain a tolerance of ±5%, compared to ±10% or more in cast acrylic.
d. Reduced waste: Uniformity minimizes offcuts and rework, improving material yield and reducing production downtime.
e. Density: Both cast and extruded acrylic have a base density of 1.19 g/cm³, but extruded sheets are often produced in 1 – 5 mm thicknesses, reducing overall weight.
f. Handling efficiency: Lightweight sheets reduce labor costs and simplify logistics, especially for mobile displays, suspended signage, and modular installations.
Disadvantages of Extruded Acrylic Sheets
i. Scratching: The surface hardness of an extruded material is lower, making it more prone to abrasions during handling, cleaning, or installation.
ii. UV degradation: Without added stabilizers, extruded acrylic can yellow or become brittle after prolonged sun exposure (within 3 – 5 years).
iii. Impact damage: It is more likely to crack or chip under mechanical stress, especially in thinner gauges.
iv. Flow lines and birefringence: Caused by internal stress during extrusion, visible under polarized light or in high-contrast environments.
v. Lower light transmittance: Usually 88% – 90%, compared to cast acrylic’s 92%. It can affect brightness and clarity in illuminated displays.
vi. Surface uniformity vs depth: Extruded sheets may appear flatter or more “plastic-like,” lacking the depth and richness of cast acrylic’s finish.
Key Differences Between Cast and Extruded Acrylic

01. Manufacturing Process
Cast Acrylic is produced by pouring liquid acrylic monomer into a mold. Curing through a slow polymerization process shapes the sheet. It’s a batch-based method that allows custom thicknesses and superior quality control.
Extruded Acrylic is made by melting acrylic pellets and continuously forcing the resin through a flat die. The sheet is then cooled and rolled to achieve uniform thickness. This process is fast, scalable, and ideal for mass production.
02. Clarity and Optical Properties
Cast Acrylic offers superior optical clarity, with light transmittance up to 92%, minimal distortion, and a rich, glass-like finish. It’s ideal for high-end displays, aquariums, and optical-grade applications.
Extruded Acrylic is slightly less clear, with light transmittance around 88% – 90%. It may show internal stress patterns, flow lines, or birefringence, especially under polarized light or when laser-cut.
03. Strength and Durability
Cast Acrylic has a higher molecular weight. It’s more resistant to impact, UV radiation, and weathering. The sheet performs well in outdoor applications, maintaining clarity and structural integrity for years.
Extruded Acrylic is prone to scratching, UV degradation, and brittleness over time. Without stabilizers, it may yellow within 3 – 5 years of sun exposure, which is suited for indoor or short-term applications.
04. Thickness and Flexibility
Cast Acrylic can be manufactured in custom thicknesses up to 2 inches (50.8 mm) or more. Such measurement offers rigidity and dimensional stability. It’s ideal for structural applications, aquariums, and load-bearing panels.
Extruded Acrylic is usually produced in thinner gauges – 1mm to 10mm. The sheet remains somewhat more flexible. That’s why extruded sheets are suitable for curved surfaces, lightweight signage, and portable displays.
05. Cost Considerations
Cast Acrylic is more expensive due to its labor-intensive, batch-based production. Prices can be 20% – 50% higher than extruded ones, especially for thicker or special-grade sheets.
Extruded Acrylic is more affordable and widely available across commercial regions. You can always opt for acrylics to accomplish any budget-sensitive or large-scale projects.
06. Machining and Fabrication
Cast Acrylic is easier to cut, engrave, and machine due to its low internal stress and consistent density. It holds its shape well after fabrication and responds beautifully to laser engraving and CNC routing.
Extruded Acrylic can be more challenging to work with. It may melt, warp, or even crack during laser cutting. However, it still performs adequately for simpler tasks like sawing, drilling, or thermoforming.

Cast vs Extruded Acrylic: Comparison Table
| Feature/Aspect | Cast Acrylic | Extruded Acrylic |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Liquid MMA poured into molds and cured slowly in batches | Melted acrylic pellets extruded continuously through a die |
| Production Speed | Slower and labor-intensive | Fast and automated |
| Flexibility | Rigid and dimensionally stable | More flexible for curved or light |
| Durability | Better UV resistance, weatherproof, impact-resistant | Prone to scratching, yellowing, and cracking |
| Surface Finish | Glossy, smooth, polishable | Smooth but less glossy |
| Machinability | Excellent for laser cutting, engraving, and CNC machining | Decent for basic cutting and forming |
| Cost Consideration | More expensive due to complex production | More affordable for budget-sensitive or large-scale projects |
| Applications | Aquariums, luxury displays, architectural glazing, awards, and outdoor signage | Retail signage, lightboxes, DIY projects, and indoor panels |
Best Uses for Cast Acrylic
Cast acrylic is a high-performance material engineered for clarity, durability, and precision. Thanks to its superior properties, the polymer excels in demanding applications across sectors.
a. Signage and Displays
Cast acrylic is the gold standard for high-end signage and visual merchandising, where clarity and surface finish directly influence brand perception.
Example: In a city’s upscale retail zone, luxury boutiques can use cast acrylic for backlit logos, product showcases, and interactive displays. Such approaches ensure visual impact and longevity.
b. Architectural Applications
It’s widely used in architectural design, especially where aesthetics and performance intersect. Applications include windows, skylights, facades, partitions, balustrades, and decorative panels.
Example: The Dubai Mall Aquarium uses cast acrylic panels over 30 inches thick to withstand water pressure while offering distortion-free viewing. It’s something extruded acrylic cannot achieve.
c. Outdoor and UV-Exposed Applications
Cast acrylic’s superior UV resistance is ideal for constant outdoor environments. Common uses include roadside signage, outdoor displays, car windows, solar panel covers, and protective shields.
Example: Government and corporate signage along a specific roadway can use cast acrylic for illuminated nameplates and directional signs, ensuring visibility and durability in harsh conditions.
d. Precision Fabrication
Cast acrylic is the preferred material for intricate machining, laser cutting, and engraving, thanks to its low internal stress and consistent density.
Use Case: Corporate awards, trophies, and custom signage often rely on cast acrylic for engraved logos, beveled edges, and polished finishes.

Best Uses for Extruded Acrylic
Extruded acrylic is a practical and cost-effective material. A high-quality sheet balances clarity, flexibility, and affordability. Ease of production goes well with budget-conscious, high-volume, and light-duty uses.
a. General Signage and Indoor Displays
Extruded acrylic is widely used in retail signage, promotional displays, and temporary installations. It’s perfect for places where visual impact is important but ultra-high clarity isn’t essential.
Example: Mobile phone retailers across big cities often use 3 mm extruded acrylic for illuminated brand panels and promotional signage—balancing clarity with affordability across dozens of outlets.
b. Protective Barriers and Shields
Extruded acrylic’s flexible nature suffices for indoor protective barriers in healthcare, office, and hospitality. Applications include sneeze guards, desk partitions, checkout shields, and counter barriers.
Example: During the COVID-19 pandemic, thousands of extruded acrylic sneeze guards were deployed in banks, pharmacies, and restaurants. They provided quick and affordable protection with visibility.
c. Furniture and DIY Projects
Extruded acrylic is a favorite among DIY enthusiasts, interior designers, and furniture makers. It enables low-cost builds like shelves, tabletops, drawer fronts, decorative panels, and lighting diffusers.
Example: Many home décor startups in the online market today deploy extruded acrylic to create minimalist wall shelves and LED-lit panels. They offer stylish solutions at competitive prices.
d. Cost-Effective Solutions
Extruded acrylic is the go-to material for budget-sensitive applications where performance demands are modest and visual perfection isn’t critical.
Example: A local electronics brand launching a new product line may use extruded acrylic display stands for a 3-month campaign. It can save up to 40% in material costs.

How to Choose Between Cast and Extruded Acrylic?
i. Consider the Application
Cast Acrylic is ideal for –
- Outdoor signage, architectural glazing, aquariums, and high-end displays.
- Projects needing distortion-free transparency, such as museum showcases or optical lenses.
- Environments with high UV exposure, humidity, or mechanical impact.
Extruded Acrylic suits –
- Indoor signage, promotional displays, and temporary installations.
- Applications where visual perfection isn’t critical, such as menu boards or light diffusers.
- Projects requiring lightweight, flexible panels for curved or modular setups.
ii. Evaluate Budget and Cost Constraints
Budget is often the deciding factor, especially for startups, seasonal campaigns, or bulk procurement. Cast Acrylic costs 20% – 50% more. It’s a premium material best reserved for long-term or high-impact applications. Extruded Acrylic offers significant savings.
iii. Think About Fabrication Needs
Fabrication requirements such as cutting, engraving, or shaping can influence material choice. Cast Acrylic is easy to machine due to its low internal stress. Extruded Acrylic is suitable for basic fabrication.
iv. Consider Durability and Longevity
If your project demands long-term performance, especially in outdoor or high-traffic environments, durability becomes a top priority.
Cast Acrylic offers –
- 10+ years of UV stability without yellowing.
- Better resistance to scratching, weathering, and impact.
Extruded Acrylic may –
- Yellow or become brittle within 3 – 5 years if exposed to sunlight.
- Be more prone to surface wear and cracking.
Conclusion
The choice between cast and extruded isn’t easy, given the similarities and rather close differences. Cast sheets come with exceptional clarity, durability, and precise machinability for long-term performance. Extruded acrylic enables uniform thickness, greater flexibility, and significant cost savings for budget-sensitive installations.
Extruded or Cast: JUMEI is Ready to Deliver
Don’t get confused with your potential options to accomplish your project. Jumei Acrylic lets you pick the best possible outcome, regardless of your necessity. We have the top-tier minds, techs, and specs to meet your satisfaction. Contact us to know more about available options.
]]>This article lets you find the top wholesale acrylic sheet suppliers in terms of quality and affordability. Explore key factors like material grade, pricing structures, delivery reliability, and customization options.
Why Choose a Top Wholesale Acrylic Sheet Supplier?
Partnering with a trustworthy manufacturer means guaranteed consistency in quality, balanced pricing, and timely delivery. Such suppliers mark a wide range of acrylic types and customization options. You’ll also enjoy streamlined procurement with reduced operational risks.
a. High-Quality Materials at Competitive Prices
Premium-grade acrylic sheets are designed to withstand wear, impact, and environmental stress. Key advantages include –
- Impact Resistance: High-quality acrylic is 10–17 times stronger than glass. No wonder it’s ideal for high-traffic areas, safety enclosures, and outdoor installations.
- UV Stability: UV-resistant variants maintain clarity and color for up to 10 years. It reduces potential yellowing and degradation in outdoor signage or architectural panels.
- Scratch Resistance: Advanced coatings extend the surface life. Such a feature is particularly beneficial in retail fixtures and furniture applications.
b. Cost Savings on Bulk Orders: Scale Without Sacrifice
Top suppliers offer tiered pricing models that reward volume and loyalty. Benefits include –
- Bulk Discounts: Savings of 10% – 25% on orders exceeding 1000 sq ft. The exact value depends on thickness, finish, and customization.
- Contract Pricing: Fixed rates for long-term clients help shield against market volatility and raw material price hikes.
- Bundled Services: Some suppliers include cutting, packaging, or freight in bulk deals. It can noticeably reduce the per-unit expense.
c. Enhanced Aesthetics: Elevating Brand and Design Impact
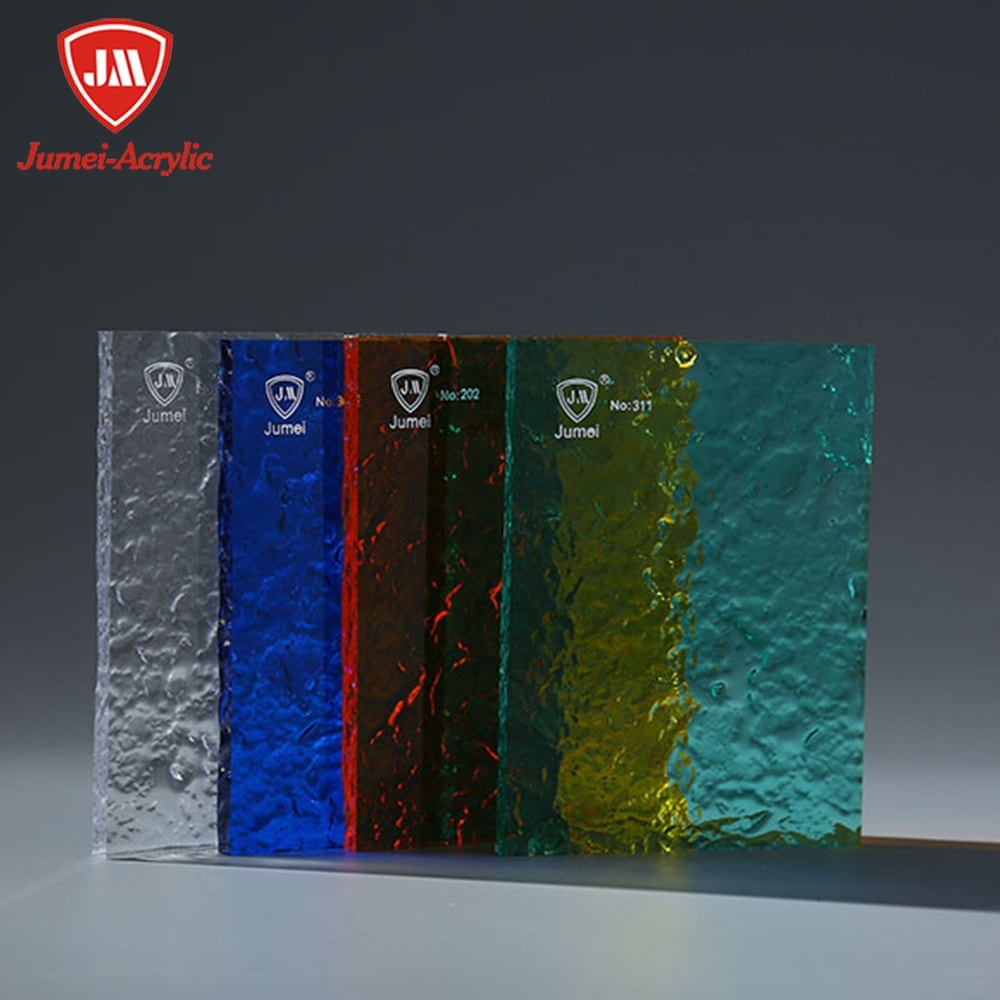

Shatter-resistant acrylic sheets offer superior clarity, color consistency, and finish options that enhance visual appeal across applications –
- Optical Clarity: Clear acrylic transmits up to 92% of visible light, rivaling glass while being lighter and safer.
- Color Fidelity: Premium sheets maintain consistent pigmentation across batches. Such features are critical for branded signage and retail displays.
- Finish Variety: Glossy, matte, frosted, and mirrored finishes allow designers to tailor aesthetics to specific environments.
d. Custom Solutions for Unique Projects
Material Selection: Choose from clear, frosted, colored, mirrored, UV-resistant, or impact-modified acrylic based on application needs.
- Thickness Options: Ranging from 1.5 mm to 25 mm, allowing for structural flexibility in everything from lightweight displays to load-bearing panels.
- Color Matching: Pantone-based customization ensures brand consistency across signage, retail fixtures, and promotional displays.
- Finish Variety: Glossy, matte, textured, satin, or anti-glare finishes tailored to lighting conditions and aesthetic goals.
- Cut-to-Size Services: Manufacturers can deploy CNC routing, laser cutting, and/or thermoforming for precise shapes and dimensions.
e. Prototyping and Design Support: From Concept to Reality
Top suppliers don’t end their responsibilities with the shipment of the materials. Their design and prototyping services help buyers –
- Visualize Concepts: CAD modeling, renderings, and mock-ups allow clients to preview how the sheets will perform in real-world settings.
- Refine Specifications: Adjust thickness, finish, or dimensions based on feedback from test evaluations of sample plexiglass sheets.
- Accelerate Approval Cycles: Prototypes help stakeholders validate design intent, reducing delays in procurement and production.

f. Reliable Service and On-Time Delivery
Almost all large-scale projects demand predictable access to high-quality materials within a steadfast schedule. A reputable supplier ensures –
- Inventory Depth: Maintains stock across multiple Plexiglas types – clear, frosted, colored, UV-resistant, and impact-modified to meet project needs.
- Batch Consistency: Delivers uniform thickness, color, and finish within extruded ones across orders, minimizing rework and installation errors.
- Production Capacity: Supports high-volume orders without compromising lead times or quality, even during peak seasons.
g. Efficient Logistics: Timing That Drives Success
On-time delivery is critical, especially in sectors where installation windows are tight and delays can trigger penalties or lost revenue. Top suppliers invest in –
- Integrated Logistics: Regional warehouses, third-party freight partnerships, and real-time tracking systems.
- Predictive Scheduling: AI-driven demand forecasting and route optimization to minimize transit delays.
- Flexible Delivery Options: Local, national, and international shipping with expedited services for urgent orders.
h. Long-Term Partnership Opportunities
Establishing a long-term relationship with a reliable supplier transforms the procurement dynamic from transactional to collaborative. Key benefits include –
- Consistent Pricing: Long-term partners often offer fixed or tiered pricing models. It protects buyers from market volatility and raw material price spikes.
- Priority Service: Repeat clients receive faster response times, dedicated account managers, and priority access to inventory during peak seasons.
- Quicker Turnaround: Familiarity with your specifications, such as preferred thickness, finish, or packaging, reduces lead times and minimizes errors.

i. Sustained Cost Efficiency: Loyalty That Pays Off
Consistent ordering from the same supplier builds trust. And trust often translates into financial benefits. Top suppliers reward loyalty through –
- Bulk Discounts: Volume-based pricing improves over time, with savings of 10–25% for repeat high-volume orders.
- Rebate Programs: Annual or quarterly rebates based on cumulative spend incentivize long-term commitment.
- Flexible Payment Terms: Long-term clients may receive extended payment windows, installment options, or credit lines.
Key Factors to Consider with Bulk Acrylic Sheets
01. Material Quality
- High Optical Clarity: Essential for signage, displays, and panels. Top-tier sheets boast light transmission rates of 92% or higher, rivaling glass while being half the weight.
- Impact Resistance: Superior acrylic sheets are 10–17 times more impact-resistant than glass, making them ideal for high-traffic environments or outdoor installations.
- UV Protection: UV-stabilized sheets prevent yellowing and degradation. Some suppliers offer 10-year warranties on UV performance, a clear indicator of material quality.
02. Industry Certifications
- ISO 9001: Ensures the supplier follows a robust quality management system.
- ASTM D4802: Specifies versatile standards for cast acrylic sheets, including mechanical strength, clarity, and thickness tolerances.
- REACH + RoHS Compliance: No-hazard production is important for European markets.
03. Material Consistency
- Thickness Uniformity: Reputable suppliers maintain tolerances within ±5%, ensuring sheets fit seamlessly into automated cutting or thermoforming workflows.
- Color Matching: For branded signage or retail fixtures, color consistency across batches is non-negotiable. Suppliers often use spectrophotometers to ensure color fidelity.
- Surface Finish: Whether glossy, matte, or textured, resources must carry or develop a uniform finish to avoid visual defects or bonding issues.

04. Product (Acrylic) Variety
- Clear Acrylic: The industry standard for display cases, windows, and protective barriers. Offers up to 92% light transmission, comparable to glass but with better impact resistance.
- Frosted Acrylic: Ideal for privacy panels, lighting diffusers, and decorative signage. Reduces glare to present and maintain translucency.
- Colored Acrylic: Available in opaque, translucent, or fluorescent variants. Used in branding, retail displays, and architectural accents.
- UV-Resistant Acrylic: Engineered for outdoor use, resisting yellowing and degradation. Some suppliers guarantee 10+ years of outdoor clarity.
- Impact-Modified Acrylic: Enhanced durability for high-traffic environments or industrial use. Often used in machine guards, automotive panels, and safety enclosures.
05. Customization Options
- Custom Sizes and Shapes: CNC cutting, laser engraving, and thermoforming to match exact dimensions.
- Color Matching: Pantone-based color customization for brand consistency in signage and retail fixtures.
- Surface Finish Options: Glossy, matte, textured, or satin finishes to suit aesthetic and functional needs.
- Possible Thickness Variability: Ranges from 1.5 mm to 25 mm, depending on some unique requirements.
06. Special Features
- Anti-Scratch Coatings: Extends surface life in high-contact environments like kiosks or furniture tops.
- Mirror Finishes: Used in interior design, point-of-sale displays, and decorative panels. Offers the look of glass with added safety.
- Fire-Retardant Grades: For compliance in construction and public installations.
- UV Filtering Layers: Protects sensitive products or environments from harmful rays in museum displays or greenhouse panels.
07. Competitive Pricing
- Material Grade vs Price: High-clarity, UV-resistant, or impact-modified sheets may cost more upfront but reduce replacement and maintenance costs over time.
- Customization Costs: Suppliers who offer CNC cutting, color matching, or special finishes may charge extra. But these services often streamline downstream production.
- Shipping and Handling: Freight costs can account for 10% – 25% of total spend for international orders. Suppliers with regional warehouses or consolidated shipping options offer better value.
08. Discounts for Bulk Orders
- Order Volume: Discounts typically start at 500–1,000 sq ft, with savings of 5–20% depending on quantity.
- Repeat Purchases: Long-term clients often receive loyalty pricing or annual rebate programs.
- Contractual Agreements: Some suppliers offer fixed pricing for 6 – 12 months, shielding buyers from market fluctuations.
09. Transparent Pricing
- Itemized Quotes: Clear breakdowns of material cost, customization charges, packaging, and freight.
- No Hidden Fees: Avoid suppliers who add unexpected surcharges for handling, palletizing, or expedited shipping.
- Digital Tools: Some have online calculators or instant quote systems, improving speed and accuracy.

10. Fast Turnaround Times
- Construction and signage projects with fixed installation schedules.
- Seasonal campaigns where delays can result in missed sales windows.
- Retail fixture replacements often require just-in-time delivery.
11. Shipping Costs
- Delivery Zones: Suppliers with regional warehouses or distribution hubs can reduce costs and lead times for local and national deliveries.
- Consolidated Shipping: Some suppliers can provide bundled freight for bulk orders. It should reduce per-unit shipping cost by 15% – 25%.
12. Packaging and Safety
- Protective Films: Applied to both sides to prevent surface damage during handling.
- Edge Guards and Corner Protectors: Essential for maintaining sheet integrity during stacking and transport.
- Moisture-Resistant Wrapping: Prevents warping in humid climates or during long-haul shipping.
- Palletization and Crating: Sheets in bulk order should be securely strapped and crated to avoid shifting and breakage.
13. Responsive Communication
- Respond to inquiries within 24 – 48 hours, offering clear answers and actionable next steps.
- Assign dedicated account managers or support reps for bulk buyers, ensuring continuity and personalized service.
- Use multiple channels (email, phone, live chat, WhatsApp) for access across time zones.
14. Pre-Sales Support
- Technical datasheets and performance comparisons to help buyers evaluate properties like clarity, tensile strength, and thermal properties.
- Material consultations to match acrylic types with project needs (UV-resistant for outdoor signage, impact-modified for industrial panels).
- Provide (manufacturer) or ask (client) for samples or mock-ups for large orders, allowing customers to test compatibility before committing.
15. After-Sales Service
- Clear return and exchange policies for defective or mismatched sheets.
- Warranty coverage on UV resistance, impact durability, or surface finish, ranging from 1 to 10 years, depending on the product.
- Technical troubleshooting for installation, bonding, or cutting issues.
16. Customer Reviews and Testimonials: Listening to the Market

Customer feedback offers real-world insights into a supplier’s strengths and weaknesses. Key benefits of reviewing testimonials include –
- Performance Validation: Reviews often highlight delivery speed, product quality, and customer service responsiveness.
- Issue Resolution: Look for patterns in how suppliers handle complaints, returns, or damaged shipments.
- Sector Relevance: Testimonials from similar industries (signage, retail fixtures, construction) provide context-specific reliability indicators.
17. Industry Reputation: Track Record
A supplier’s history in the acrylic sheet market speaks volumes about their operational stability and expertise. Consider –
- Years in Business: Suppliers with 10+ years in the industry often have refined manufacturing processes and robust logistics networks.
- Client Portfolio: Serving well-known brands or government projects signals credibility and capacity.
- Certifications and Awards: Recognition from trade associations or compliance bodies (ISO, ASTM) reinforces trust.
18. Case Studies and Projects: Proof of Capability
- Project Scope: Whether the supplier can handle high-volume orders, tight deadlines, or custom specifications.
- Problem-Solving Ability: How they adapt to challenges like material shortages, design changes, or logistics disruptions.
- Sector Expertise: Experience in your specific industry (retail, construction, automotive) ensures smoother collaboration.
19. Sustainable and Recycled Acrylic Options
Recycled acrylic sheets are made by reprocessing post-industrial or post-consumer acrylic waste. They are widely implemented as a committed message towards the planet. Key benefits include –
- Up to 90% reduction in raw material usage, depending on the recycling process.
- Lower carbon emissions during production compared to virgin acrylic.
- Reduced landfill waste, supporting circular economy goals.
20. Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
Eco-conscious suppliers go beyond materials as they optimize their entire production process. Look for vendors who –
- Use closed-loop water systems to reduce water waste.
- Implement energy-efficient machinery and renewable energy sources.
- Minimize offcuts and scrap through precision cutting and batch optimization.
- Offer take-back programs for unused or damaged sheets.
21. Eco-Certifications for Verifications
Certifications provide third-party validation of a supplier’s sustainability claims. Key labels to look for include –
- ISO 14001: Indicates a certified environmental management system.
- Global Recycled Standard (GRS): Verifies recycled content and responsible social, environmental, and chemical practices.
- RoHS & REACH Compliance: No hazardous substances that meet EU safety standards.
- GreenGuard Certification: Confirms low chemical emissions, ideal for indoor applications like retail fixtures and furniture.

How to Get the Best Deal on Wholesale Acrylic Sheets
Get the best deal on wholesale acrylic sheets by comparing multiple suppliers based on quality, pricing, and customization. Look for bulk discounts, loyalty programs, and transparent pricing. Prioritize suppliers with strong customer reviews, fast turnaround times, and consistent product quality.
i. Volume Discounts: Scale Drives Savings
Bulk purchasing is one of the most effective levers for negotiating better rates. Top suppliers typically offer tiered pricing structures based on square footage, sheet count, or monthly spend.
- Understand Pricing Tiers: Discounts often begin at 500 – 1000 sq ft. Standard savings range from 10% to 25% depending on acrylic type, thickness, and finish.
- Negotiate Repeat Order Terms: Suppliers may offer deeper discounts for recurring orders or annual contracts, especially if you commit to quarterly volumes.
- Bundle Customization and Freight: Some suppliers include cutting, packaging, or delivery in bulk deals, reducing your per-unit cost.
ii. Promotions and Special Offers: Timing Is Everything
Seasonal promotions, clearance sales, and supplier incentives can offer significant savings. It’s notably true for flexible or opportunistic buyers. Key strategies include –
- Monitor Seasonal Trends: Suppliers often run promotions before major holidays (Christmas, Chinese New Year) or fiscal year-end to clear inventory.
- Subscribe to Supplier Alerts: Email newsletters, WhatsApp updates, or trade platform notifications often include flash deals or limited-time offers.
- Negotiate Add-Ons: During promotional periods, suppliers may include free samples, expedited shipping, or extended warranties as part of the deal.

iii. Test Samples: Minimize Risk, Maximize Confidence
Before placing a bulk order, always request physical samples to verify that the acrylic sheets meet your project’s technical and aesthetic requirements. It lets you –
- Assess Material Quality: Confirm optical clarity, surface smoothness, and rigidity for easy applications.
- Verify Functional Features: Test UV resistance, impact strength, or anti-scratch coatings under real-world conditions.
- Check Compatibility: Ensure the sheet performs well with your cutting, bonding, or printing equipment.
iv. Evaluate Samples: Precision Matters
Once the samples arrive, evaluate them against your project’s specifications. Key criteria include –
- Clarity: For display cases or work signage, look for light transmission rates of 90% – 92%.
- Finish: Get or read tips on glossy, matte, frosted, or textured finishes that align with your visual and functional goals.
- Color Accuracy: For branded applications, discover color fidelity under various lighting conditions.
- Thickness Consistency: Use calipers to measure uniformity across the sheet. Tolerances should be within ±5% for precision applications.
v. Comparing Acrylic against Alternatives
No need to stick yourself to acrylic only without knowing what puts it ahead of others. There are several plastic and glass-like alternatives that are used to overcome acrylic-oriented challenges.
- Polycarbonate is often considered the premium alternative to acrylic, especially in high-impact or safety-critical environments.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) is another viable alternative for thermoforming and food-safe items.
- Even plexiglass, Perspex, and Lucite can lend a hand as acrylic alternatives. The branded PMMA products have distinctive pros.
Conclusion
Choosing the right wholesale acrylic sheet supplier seems like a procurement task from the start. However, it has become a strategic decision that impacts quality, cost-efficiency, and project success. Each factor plays a vital role in delivering durable, visually appealing, and budget-aligned outcomes.
JUMEI is Ready to Meet Quality and Affordability Expectations
You’ll find many suppliers on the market, only to realize that not many can balance pricing and quality. That’s where Jumei Acrylic outshines the competition with top-tier quality, performance, and innovation for the right price. Contact us to let our well-experienced team answer your questions.
]]>